EASY
Earn 100
There is a galvanometer of resistance has divisions and a sensitivity . It can be converted into a voltmeter to read by connecting
(a)resistance in series.
(b) in parallel.
(c) is series.
(d) is parallel.
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Current Electricity
HARD
A moving coil galvanometer has 50 turns and each turn has an area . The magnetic field produced by the magnet inside the galvanometer is . The torsional constant of the suspension wire is . When a current flows through the galvanometer, a full scale deflection occurs if the coil rotates by . The resistance of the coil of the galvanometer is . This galvanometer is to be converted into an ammeter capable of measuring current in the range . For this purpose, a shunt resistance is to be added in parallel to the galvanometer. The value of this shunt resistance, in ohms, is . Write the value of , where is the greatest integer function.
EASY
A galvanometer with its coil resistance requires a current of for its full deflection. In order to construct an ammeter to read up to a current of the approximate value of the shunt resistance should be:
EASY
Sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer is . If a shunt of of the resistance of galvanometer is connected to moving coil galvanometer, its sensitivity becomes
MEDIUM
A galvanometer has a 50 division scale. Battery has no internal resistance. It is found that there is deflection of 40 divisions when Deflection becomes 20 divisions when resistance taken from resistance box is 4900 Ω. Then we can conclude :
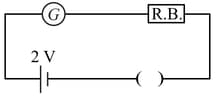
Note: This question is awarded as the bonus. Now the question is corrected.
MEDIUM
The galvanometer deflection, when key is closed but is open, equals (see figure). On closing also and adjusting to the deflection in galvanometer becomes The resistance of the galvanometer is, then, given by [Neglect the internal resistance of battery]:
MEDIUM
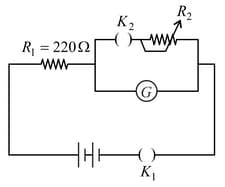
To know the resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method, a battery of emf and resistance is used to deflect the galvanometer by angle . If a shunt of resistance is needed to get half deflection the , and are related by the equation:
EASY
When a current of is passed through a galvanometer having a coil of resistance , it shows full-scale deflection. The value of the resistance to be put in series with the galvanometer to convert it into a voltmeter of range is:
MEDIUM
A moving coil galvanometer has a coil with turns and area It uses a torsion band of torsion constant The coil is placed in a magnetic field B parallel to its plane. The coil deflects by for a current of The value of B (in tesla) is approximately:
EASY
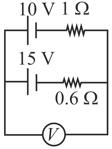
A battery with internal resistance and a battery with internal resistance are connected in parallel to a voltmeter (see figure). The reading in the voltmeter will be close to:
EASY
The reason a moving coil galvanometer cannot be used with an alternating current is that
MEDIUM
A resistance is connected to a battery of . A galvanometer of resistance is to be used as an ammeter to measure current through the resistance, for this a resistance is connected to the galvanometer. Which of the following connections should be employed if the measured current is with in of the current without the ammeter in the circuit?
EASY
A circuit contains an ammeter, a battery of 30 v and a resistance 40.8 ohm all connected in series. If the ammeter has coil of resistance 480 ohm and a shunt of 20 ohm, the reading in the ammeter will be:
HARD
A moving coil galvanometer, having a resistance produces full scale deflection when a current flows through it. This galvanometer can be converted into (i) an ammeter of range 0 to by connecting a shunt resistance to it and (ii) into a voltmeter of range 0 to by connecting a series resistance to it. Then,
MEDIUM
A galvanometer having a coil resistance of gives a full scale deflection, when a current of is passed through it. The value of the resistance, which can convert this galvanometer into ammeter giving a full scale deflection for a current of , is:
HARD
A galvanometer of resistance has divisions on its scale and has sensitivity of . It is to be converted to voltmeter with three ranges, of and The appropriate circuit to do so is:
MEDIUM
A moving coil galvanometer has resistance and it indicates full deflection at current. A voltmeter is made using this galvanometer and a resistance. The maximum voltage, that can be measured using this voltmeter, will be close to:
MEDIUM
The resistance of a galvanometer is and the maximum current which can be passed through it is What resistance must be connected to it in order to convert it into an ammeter of range
EASY
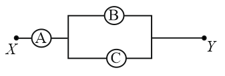
, and are voltmeters of resistance , and respectively as shown in the figure. When some potential difference is applied between and , the voltmeter readings are and respectively. Then:
EASY
This question has and . Of the four choices given after the Statements, choose the one that best describes the two Statements.
Higher the range, greater is the resistance of ammeter.
To increase the range of ammeter, additional shunt needs to be used across it.
MEDIUM
A galvanometer, whose resistance is , has divisions in it. When a current of A passes through it, its needle (pointer) deflects by one division. To use this galvanometer as a voltmeter of range it should be connected to a resistance of:

