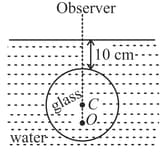
There is a small air bubble inside a glass sphere of radius 5 cm. The bubble is at at below the surface of the glass. The sphere is placed inside water such that the top surface of glass is below the surface of water. The bubble is viewed normally from air. Find the apparent depth of the bubble.


Important Questions on Ray Optics
A small object of length lies along the principal axis of a spherical glass of radius and refractive index is . The object is seen from air along the principal axis from left. The distance of object from the centre is . Find the size of the image. Is it real, inverted?
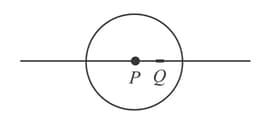
A narrow parallel beam of light is incident paraxially on a solid transparent sphere of radius kept in air. What should be the refractive index if the beam is to be focused
(a) at the farther surface of the sphere,
(b) at the centre of the sphere.
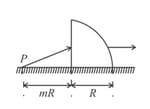
A quarter cylinder of radius and refractive index is placed on a table. A point object is kept at a distance of from it. Find the value of for which a ray from will emerge parallel to the table as shown in the figure.
The focal length of lens shown in the figure. Solve for three cases
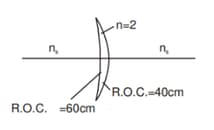
A thin lens, made of a material of refractive index has a medium of refractive index on one side and a medium of refractive index on the other side. The lens is biconvex and the two radii of curvature have equal magnitudes, . A beam of light travelling parallel to the principal axis is incident on the lens. Where will the image be formed, if the beam is incident from
(a) the medium and
(b) from the medium ?
Two glasses with refractive indices of are used to make two identical double-convex lenses.
(i) Find the ratio of their focal lengths.
(ii) How will each of these lenses act on a ray parallel to its optical axis if the lenses are submerged.
