Thermodynamic equilibrium is completely defined by the specifications of-
Important Questions on Heat and Thermodynamics
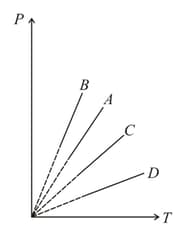
Pressure versus temperature graph of an ideal gas at constant volume is shown by the straight-line . Now mass of the gas is doubled and the volume is halved then the corresponding pressure versus temperature graph will be shown by the line
Consider the following thermodynamical variables
(i) Pressure
(ii) Internal Energy
(iii) Volume
(iv) Temperature
Out of these, the intensive variable(s) is (are)
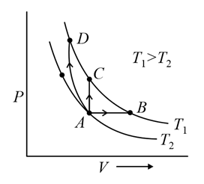
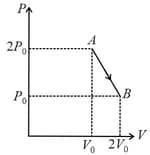
Three different processes that can occur in an ideal monoatomic gas are shown in the vs diagram. The paths are labelled as and . The change in internal energies during these process are taken as and and the work done as and . The correct relation between these parameters are:
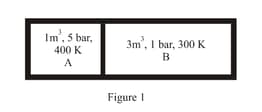
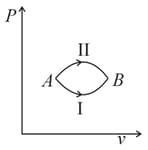
A system goes from to via two processes and shown in the figure. If and are the changes in internal energies in the processes I and Il respectively
(Neglect the heat loss through the lead wires of the heater. The heat capacity of the heater coil is also negligible)

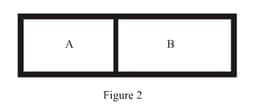
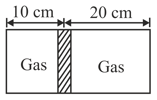
Diagram shows a horizontal cylindrical container of length , which is partitioned by a tight-fitting separator. The separator is diathermic but conducts heat very slowly. Initially the separator is in the state shown in the diagram. The temperature of left part of cylinder is and that on right part is . Initially the separator is in equilibrium. As heat is conducted from right to left part, separator displaces to the right. Find the displacement of separator(in ) after a long time when gases on the two parts of cylinder are in thermal equilibrium.
Explain why
(a) Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2 if brought in thermal contact do
not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2 )/2.
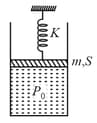
In the arrangement shown in figure. Gas is thermally insulated. An ideal gas is filled in the cylinder having pressure (> atmospheric pressure ). Spring of force constant is initially unstretched. Piston of mass and area is frictionless. In equilibrium piston rises up a distance , then
Represent the union of two sets by Venn diagram for each of the following.
is a prime number between and
is an odd number between and

