This diagram shows a current-carrying wire frame placed between a pair of magnets on a yoke. A pointer is attached to the wire.
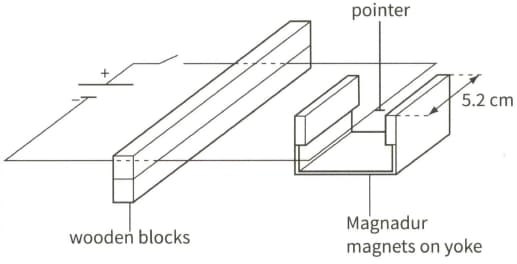
A current of in the wire causes the pointer to move vertically upwards. A small paper tape is attached to the pointer and the current is adjusted until the weight of the paper tape causes the pointer to return to its initial position (with no current and no paper tape). The mass of the paper tape is The section of the wire between the poles of the magnetic has a length of . Calculate the force on the wire due to the magnetic field when it Carries a current of


Important Questions on Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetism
This diagram shows a current-carrying wire frame placed between a pair of Magnadur magnets on a yoke. A pointer is attached to the wire.
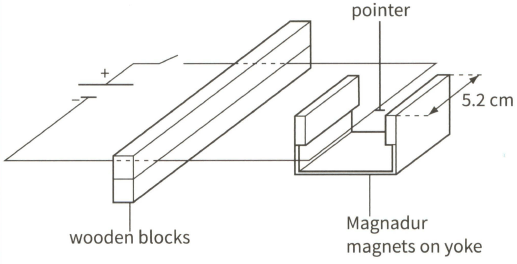
A current of 8.5 A in the wire causes the pointer to move vertically upwards. A small paper tape is attached to the pointer and the current is adjusted until the weight of the paper tape causes the pointer to return to its initial position (with no current and no paper tape). The mass of the paper tape is The section of the wire between the poles of the magnetic has a length of .
(c) Calculate the magnetic flux density of the magnetic field between
the poles of the magnet.
This diagram shows a current-carrying wire frame placed between a pair of magnets on a yoke. A pointer is attached to the wire.
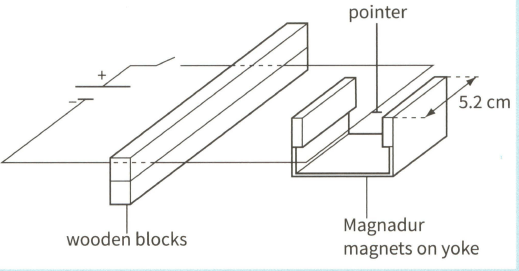
A current of In the wire causes the pointer to move vertically upwards. A small paper tape is attached to the pointer and the current is adjusted until the weight of the paper tape causes the pointer to return to its initial position (with no current and no paper tape). The mass of the paper tape is The section of the wire between the poles of the magnetic has a length of . Describe what happens to the frame if low-frequency alternating current passes through the wire.
At a certain point on the Earth's surface, the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is A piece of wire long and weight lies in an east- west direction on a laboratory bench. When a large current flows in the wire, the wire just lifts off the surface of the bench. State the direction of the current in the wire.
At a certain point on the Earth's surface, the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is A piece of wire long and weight lies in an east- west direction on a laboratory bench. When a large current flows in the wire, the wire just lifts off the surface of the bench. Calculate the minimum current needed to lift the wire
from the bench.
This diagram shows a fixed horizontal wire passing centrally between the poles of a permanent magnet that is placed on a top-pan balance.
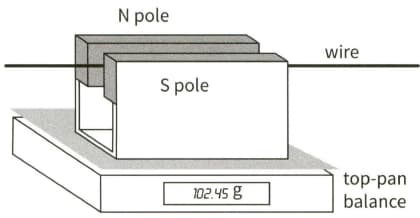
With no current flowing, the balance records a mass of When a current of flows in the wire, the balance records a mass of
(a) Explain why the reading on the top-pan balance decreases
when the current is switched on.
This diagram shows a fixed horizontal wire passing centrally between the poles of a permanent magnet that is placed on a top-pan balance.
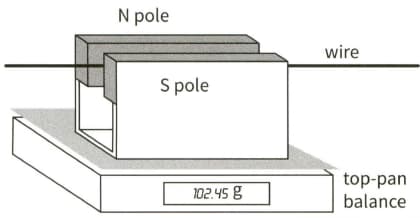
With no current flowing, the balance records a mass of When a current of flows in the wire, the balance records a mass of
(b) State and explain the direction of the current flow in the wire.
This diagram shows a fixed horizontal wire passing centrally between the poles of a permanent magnet that is placed on a top-pan balance.
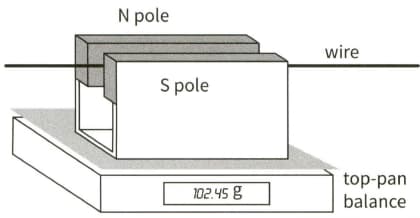
With no current flowing, the balance records a mass of When a current of flows in the wire, the balance records a mass of
(c) The length of the wire in the magnetic field is Calculate the average magnetic flux density between the poles of the magnet.
