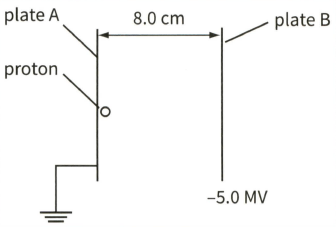
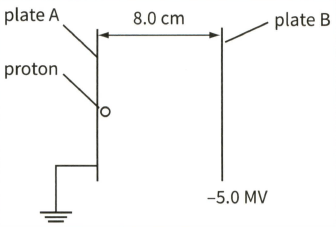
This diagram shows a proton as it moves between two charged parallel plates. The charge on the proton is
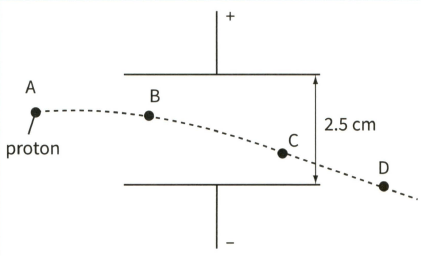
Calculate the potential difference between the plates.
The force on the proton when it is at position is .


Important Questions on Uniform Electric Fields
Define what is meant by the electric field strength at a point.In a particle accelerator, a proton, initially at rest, is accelerated between two metal plates, as shown.
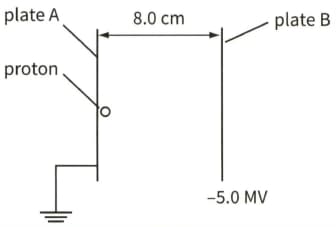
Calculate the force on the proton due to the electric field in the given figure.
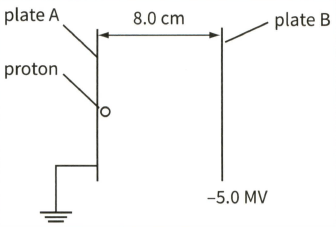
Calculate the work done on the proton by the electric field when it moves from plate A to plate B.
State the energy gained by the proton.
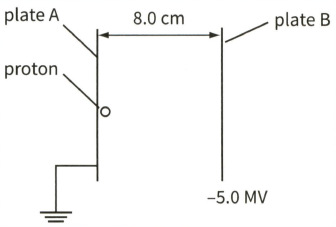
Assuming that all the energy is converted to kinetic energy of the proton, calculate the speed of the proton when it reaches plate.
(Charge on a proton mass of a proton .)
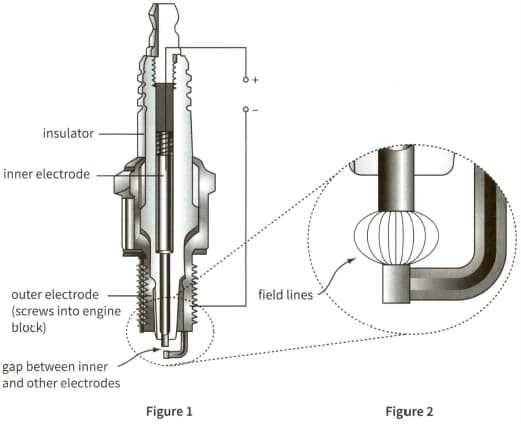
This diagram shows the structure of a spark plug in an internal combustion engine. The magnified section shows the end of the spark plug, with some of the lines of force representing the electric field.
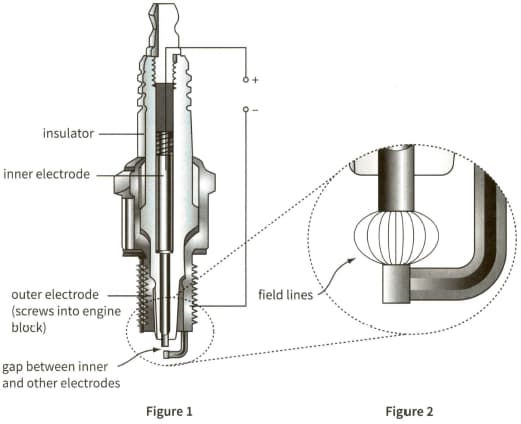
Copy the field lines from the diagram. On your copy, draw arrows on the lines of force to show the direction of the field.
This diagram shows the structure of a spark plug in an internal combustion engine. The magnified section shows the end of the spark plug, with some of the lines of force representing the electric field.
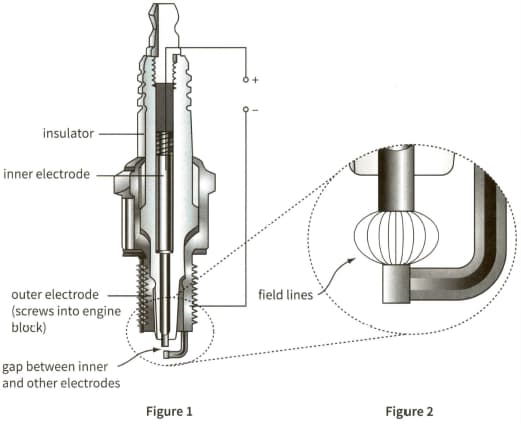
What evidence does the diagram give that the field is strongest near the tip of the inner electrode?
The gap between the inner and outer electrodes is $1.25 \mathrm{~mm}$ and a field strength of $5.0 \times 10^{6} \mathrm{NC}^{-1}$ is required for electrical breakdown. Estimate the minimum potential difference that must be applied across the inner and outer electrodes for a spark to be produced. (You may treat the two electrodes as a pair of parallel plates.)