This diagram shows a stationary wave on a string.

(a) On a copy of the diagram, label one node (N) and one antinode (A).


Important Questions on Stationary Waves
This diagram shows a stationary wave on a string.
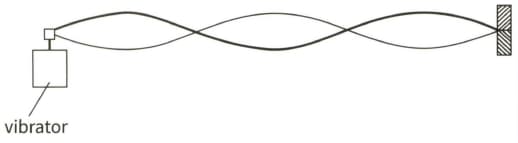
(b) Mark on your diagram the wavelength of the progressive wave and label it .
This diagram shows a stationary wave on a string.

(c) The frequency of the vibrator is doubled. Describe the changes in the stationary wave pattern.
A tuning fork that produces a note of 256Hz is placed above a tube that is nearly filled with water. The water level is lowered until resonance is first heard.
(a) Explain what is meant by the term resonance.
A tuning fork that produces a note of 256Hz is placed above a tube that is nearly filled with water. The water level is lowered until resonance is first heard.
(b) The length of the column of air above the water when resonance is first heard is 31.2cm.
Calculate the speed of the sound wave.
(b) This diagram shows an experiment to measure the speed of a sound in a string. The frequency of the vibrator is adjusted until the stationary wave shown is formed.
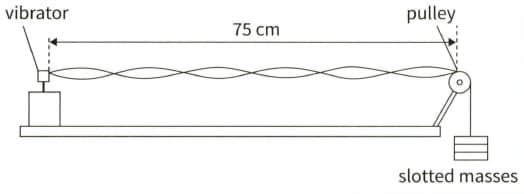
(i) On a copy of the diagram, mark a node (label it N) and an antinode (label it A).
(b) This diagram shows an experiment to measure the speed of a sound in a string. The frequency of the vibrator is adjusted until the stationary wave shown is formed.
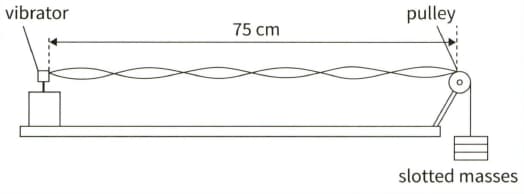
(ii) The frequency of the vibrator is 120Hz. Calculate the speed at which a progressive wave would travel along the string.
