This is about the manufacture of ammonia. Why is the mixture passed over iron?

Important Questions on Some Non-Metals and their Compounds
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.

What does this diagram tell you?
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
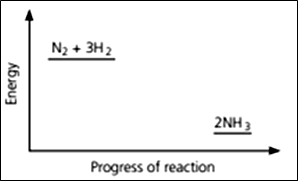
Explain why high temperatures are not used in the manufacture of ammonia.
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
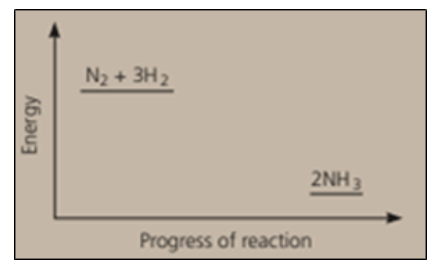
The reaction is reversible, and reaches equilibrium. Explain very clearly what the two terms in italics mean.
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
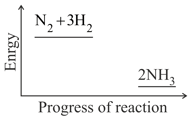
What effect does a catalyst have on an equilibrium reaction?
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
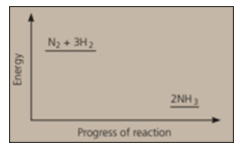
Which catalyst is used in the Haber's process?
Nitrogen and hydrogen are converted to ammonia in the Haber process: . Below is the energy level diagram for the reaction.
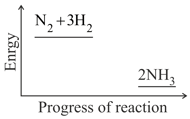
What effect does this catalyst have on the yield of ammonia?
