MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
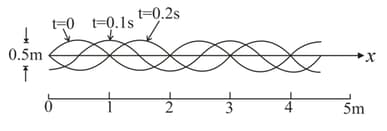
Three consecutive flash photographs of a travelling wave on a string are reproduced in the figure here? The following observations are made. Mark the one which is correct. (Mass per unit length of the string )

50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Wave Motion on a String
HARD
NEET
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
A copper wire is held at the two ends by rigid supports. At the wire is just taut, with negligible tension. The speed of transverse waves in this wire at is:
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
MEDIUM
NEET
IMPORTANT
EASY
NEET
IMPORTANT
