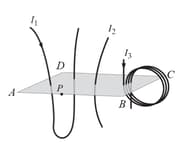
Three distinct current carrying wires intersect a finite rectangular plane . The current in the left wire and the loop is . The direction of current in left-most wire and right-most loop is downwards as shown in the figure. The current through the middle wire is adjusted so that the path integral of the total magnetic field along the perimeter of the rectangle is zero, that is, Then the current is


Important Questions on Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
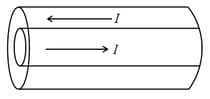
The figure shows a long coaxial cable in which a current flows down through the inner cylinder of radius and the same current flows back up through the outer cylinder of radius . The cylinders are insulated from each other and the current is uniformly distributed over the area of the cross-section in each cylinder. The strength of the magnetic field at a distance from the axis of the cable is
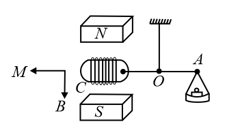
A small coil with turns is mounted on one end of a balance beam and introduced between the poles of an elctromagnet as shown in the figure. The cross sectional area of coil is , length of arm of the balance beam is . When there is no current in the coil the balance is in equilibrium. On passing a current through the coil the equilibrium is restored by putting the additional counter weight of mass on the balance pan. Find the magnetic induction at the spot where coil is located.
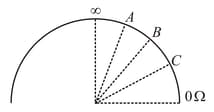
An ohm meter measures the resistance placed between its leads. This resistance reading is indicated by a galvanometer that operates on current. The ohm meter has an internal source of voltage to create the necessary current to operate the galvanometer and also has an appropriate resistor to allow just the right amount of current through the galvanometer. A simple ohm meter is shown here. When there is infinite resistance, there is zero current through a galvanometer, and it points in middle. If the test leads of this meter arc directly shorted (zero / resistance), the galvanometer will give full deflection.
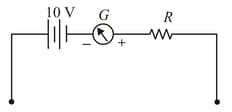
Galvanometer specification:
Resistance of galvanometer
Full-scale current
Total number of division
If an unknown resistance is placed between two leads and the needle deflects up to (mid of scale), then resistance is equal to
