Three moles of an ideal gas at pressure and temperature is isothermally expanded to twice its initial volume. It is then compressed at a constant pressure to its original volume.
Sketch and diagram for the complete process.
Calculate not work done by the gas.
Calculate net heat supplied to the gas during the complete process.
(Write your answer in terms of gas constant )
Sketch and diagram for the complete process.
Calculate not work done by the gas.
Calculate net heat supplied to the gas during the complete process.

Important Questions on Laws of Thermodynamics
Sketch the process on a diagram.
What are the final volumes and pressure of the gas?
What is the work done by the gas?
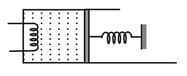
An ideal monoatomic gas is confined by a spring-loaded massless piston of the cross-section . Initially, the gas is at and occupies a volume of and the spring is in its relaxed state. The gas is heated by an electric heater until the piston moves out slowly without friction by . Calculate
the final temperature of the gas and
the heat supplied by the heater. The force constant of the spring is , atmospheric pressure is . The cylinder and the piston are thermally insulated.
Find the work performed by the gas to increase its internal energy by .
Find the molar specific heat of the gas.
Find the work done by the gas if the temperature increases by .
Also, find the molar specific heat of the gas.
Calculate the molar specific heat for the process.
Find the work done by two moles of gas if the temperature changes from to .