MEDIUM
Earn 100
Three stationary particles of masses and are under the action of same constant force for the same time. If , the variation of momentum of particles with time for each will be correctly shown as
(a)
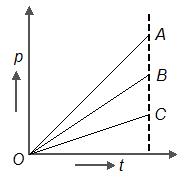

(b)
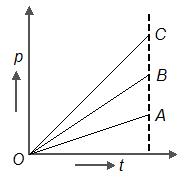

(c)
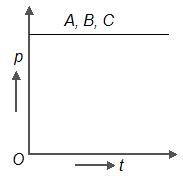

(d)
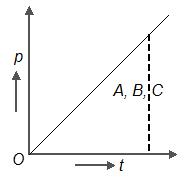

50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Force
MEDIUM
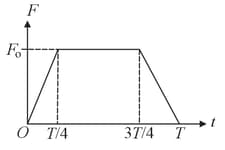
EASY
MEDIUM
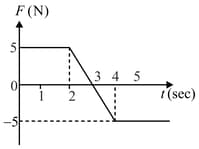
A block of the mass of is moving on the -axis. A force acting on the block is shown. The velocity of the block at time is . What is the speed of the block at time ?
EASY
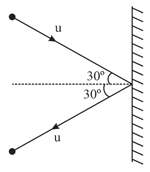
HARD
At time second, a particle of mass 3 kg has position vector metre, where The impulse of the force during the time interval is -
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
is
EASY
EASY
EASY
A particle of mass m is moving with a uniform velocity It is given an impulse such that its velocity becomes The impulse is equal to :
EASY
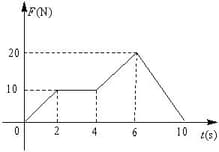
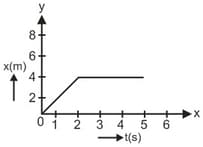
The velocity of the particle after 10 s is
HARD
EASY
A particle of mass m is moving with a uniform velocity It is given an impulse such that its velocity becomes The impulse is equal to :
EASY
HARD
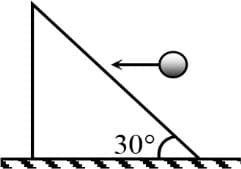
MEDIUM
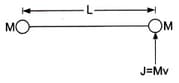
MEDIUM
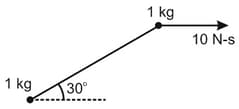
EASY

