Tin is obtained from cassiterite by reduction with coke. Use the data given below to determine the minimum temperature (in ) at which the reduction of cassiterite by coke would take place.
Assume that the enthalpies and the entropies are temperature independent.

Important Questions on Thermodynamics
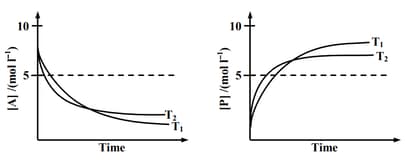
If , the correct statement(s) is (are)
(Assume are independent of temperature and ratio of is greater than . Here H, S , G and K are enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs energy and equilibrium constant, respectively.)
The surface of copper gets tarnished by the formation of copper oxide. gas was passed to prevent the oxide formation during heating of copper at 1250 K. However, the gas contains 1 mole % of water vapour as impurity. The water vapour oxidises copper as per the reaction given below:
Is the minimum partial pressure of (in bar) needed to prevent the oxidation at . The magnitude of value of is ____.
(Given: total pressure = 1 bar, R (universal gas constant) are mutually immiscible.
At
)
Round off the answer up to the nearest integer.
The standard state means that the pressure should be 1 bar, and substance should be pure at a given temperature. The conversion of graphite [ (graphite)] to diamond [ (diamond)] reduces its volume by . If (graphite) is converted to (diamond) isothermally at , the pressure at which (graphite) is in equilibrium with (diamond), is
[Useful information: ]
Enthalpy of dissociation of acetic acid obtained from the Expt. 2 is
(: pressure, : volume, : temperature, : enthalpy, : entropy)
