To determine the approximate focal length of the given convex lens by focusing a distant object (say, a signboard), you try to focus the image of the object on a screen. The image you obtain on the screen is always :

Important Questions on Light : Reflection and Refraction
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
AB is the incident ray on a glass slab.
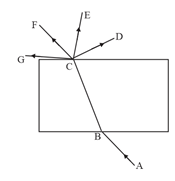
The emergent ray is:
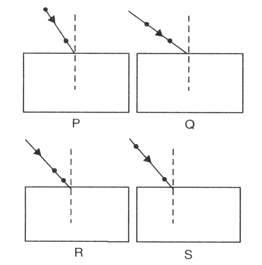
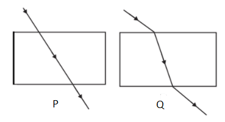
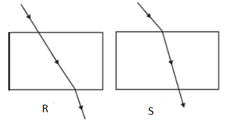
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular slab traced by four students are shown by figures P, Q, R and S. Which one of them is correct?
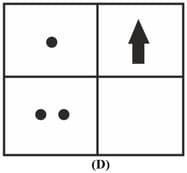
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens,
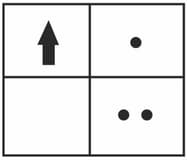
the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
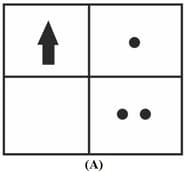
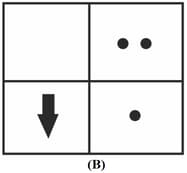
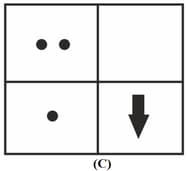
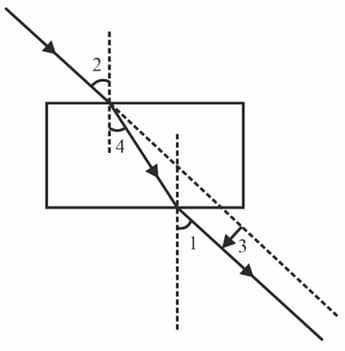
The correct sequencing of angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits and is:
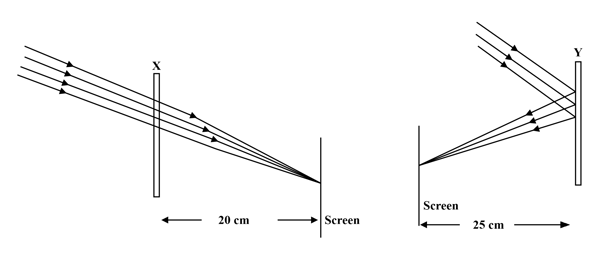
A student very cautiously traces the path of a ray through a glass slab for different values of the angle of incidence (). He then measures the corresponding values of the angle of refraction () and the angle of emergence () for every value of the angle of incidence. On analysing these measurements of angles, his conclusion would be:
