Total number of degrees of freedom of a rigid diatomic molecule is
Important Questions on Kinetic Theory
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature obeys Maxwell's distribution.
Statement II : In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature equals the translational kinetic energy for each molecule.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Using equipartition of energy, the specific heat (in ) of Aluminium at high temperature can be estimated to be (atomic weight of Aluminium )
(R-Universal gas constant)
Match the ratio for ideal gases with different type of molecules:
| Molecule Type | |
| (A) Monoatomic | (I) |
| (B) Diatomic rigid molecules | (II) |
| (C) Diatomic non-rigid molecules | (III) |
| (D) Triatomic rigid molecules | (IV) |
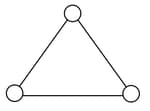
Consider a gas of triatomic molecules. The molecules are assumed to be triangular and made of massless rigid rods whose vertices are occupied by atoms. The internal energy of a mole of the gas at temperature T is:

