HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Two molal solutions are prepared by dissolving a non-electrolyte non-volatile solute separately in the solvents and . The molecular weights of the solvents are and , respectively where . The relative lowering of the vapour pressure of the solution in is times that of the solution in . Given that the number of moles of solute is very small in comparison to that of solvent, the value of is:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Solutions
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
EASY
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Consider the following terms (molality):
Terms which can be expressed in degree (temperature) are
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
What is the normal boiling point of the solution represented by the phase diagram?
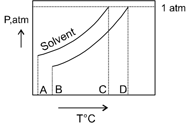
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
Density of solution of a non-electrolyte is . If is , solution freezes at
MEDIUM
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
HARD
JEE Main/Advance
IMPORTANT
