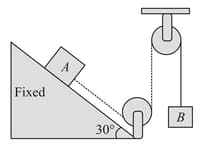
Two blocks and of equal mass are connected through a massless string and arranged as shown in figure. The wedge is fixed on horizontal surface. Friction is absent everywhere. When the system is released from rest,


Important Questions on Newton's Laws of Motion I
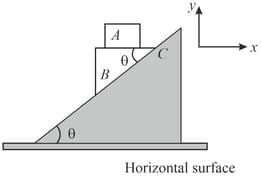
In the figure shown, all the surfaces are smooth. All the blocks , and are movable, -axis is horizontal and -axis is vertical, as shown. Just after the system is released from the position as shown,
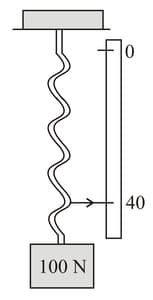
An ideal spring, with a pointer attached to its end, hangs next to a scale. With weight attached and in equilibrium, the pointer indicates on the scale, as shown. Using a weight instead results in on the scale. Using an unknown weight instead results in on the scale. Find the value of .
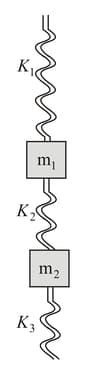
Find the value of in terms of spring constants for this to happen.
If and and acceleration of the elevator is , find the tension in the middle spring in the final equilibrium with respect to the lift.
The tension in the given spring is

A spring balance and a physical balance are kept in a lift. In these balances, equal masses are placed. Now, if the lift starts moving upwards with constant acceleration, then,
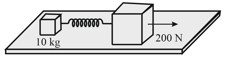
The masses of and , respectively, are connected by a massless spring, as shown in the figure. A force of acts on the mass. At the instant shown, the mass has acceleration . What is the acceleration of mass?
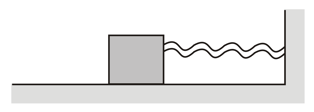
An ideal spring is compressed and placed horizontally between a vertical fixed wall and a block, free to slide over a smooth horizontal tabletop as shown in the figure. The system is released from rest. The graph which represents the relation between the magnitude of the acceleration of the block and the distance travelled by it (as long as the spring is compressed) is,
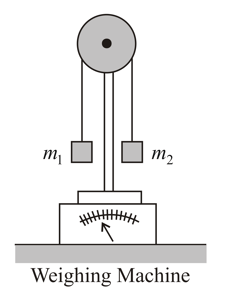
Two blocks of masses and , which are connected with a light string, are placed over a frictionless pulley. This set-up is placed over a weighing machine, as shown. Three combinations of masses and are used. In the first case, and , in second case, and and in the third case, and . The masses are held stationary initially and then released. If the readings of the weighing machine after the release, in three cases, are and , respectively, then,