HARD
Earn 100
Two bodies of equal mass m are heated at a uniform rate under identical conditions. Their change in temperatures are shown. Then
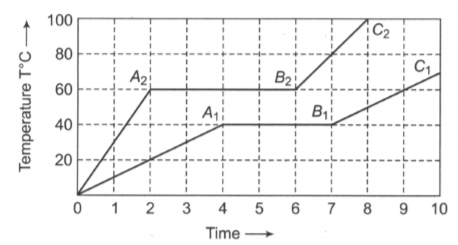
(i) the ratio of melting points of the substances is 1.5
(ii) the ratio of their latent heats is
(iii) the ratio of specific heat of two substances is in solid-state
(iv) the ratio of specific heat of two substances is 2 in a liquid state.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)All
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
EASY
Heat required to melt of ice is . A man melts of ice by chewing in one minute. His power is______
HARD
A thermally insulated cubical box of side length and wall thickness containing of ice is closed on all sides. The mass of ice melted in hours is (Thermal conductivity of the material of the box latent heat of ice and ambient temperature )
EASY
EASY
(Latent heat of ice is and )
MEDIUM
[ Specific heat of water Latent heat of water ]
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
[Take specific heat of water and latent heat of steam
EASY
HARD
(Specific heat of water is and the density of water is )
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
HARD
, where is a constant with appropriate dimension while is a constant with dimension of temperature. The heat capacity of the metal is:
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY

