Two bodies of mass and are moving with equal kinetic energies. The ratio of magnitude of their linear momentum is :
Important Questions on Work, Energy and Power
Two bodies having same linear momentum have ratio of kinetic energy as . Find the ratio of masses of these bodies.
A policeman fires a bullet of mass with a speed of , in a wooden piece of thickness . The bullet leaves the wooden piece with only of its initial kinctic energy. By how much percentage has the speed of the bullet been reduced?
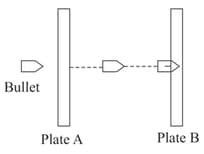
A bullet of mass pierces through a plate of mass and then gets embedded into a second plate of mass as shown in the figure. Initially the two plates and are at rest and move with same velocity after collision. The percentage loss in the initial kinetic energy of the bullet when it is between the plates and is_______. (Neglect any loss of material of the plates during the collision)
A body is dropped on ground from a height and after hitting the ground, it rebounds to a height . If the ratio of velocities of the body just before and after hitting ground is , then percentage loss in kinetic energy of the body is . The value of is _____.
A bullet of mass having initial kinetic energy is shot inside a long swimming pool as shown in the figure. If it's kinetic energy reduces to within , the minimum length of the pool, the bullet has to travel so that it completely comes to rest is


