EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
Two elastic rods are joined between fixed supports as shown in diagram. Condition for no change in the lengths of individual rods with the increase of temperature ( = linear expansion coefficient, A1, A2 = area of rods, y1, y2 = Young's modulus) is
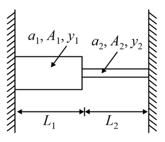
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
23.08% studentsanswered this correctly

Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
At the hole in a steel plate has a diameter of A cylinder of diameter exactly at is to be slide into the hole. To what temperature the plate must be heated. (Given: )
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
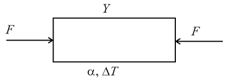
A rod is acted by two equal forces as shown in the figure. The coefficient of thermal expansion of the rod is and area of cross section is . When the temperature the rod is increased by , the length of the rod does not change. The young's modulus will be.
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
A copper rod of length at is placed on a smooth surface. Now the rod is heated up to . Find the longitudinal strain developed. (Let, coefficient of linear expansion)
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
How much should the temperature of a brass rod be increased so as to increase its length by ? (Given for brass is ).
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Water falls from a height of 500 m. What is the rise in temperature of water at the bottom if whole energy is used up in heating water?
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
Two moles of oxygen is mixed with eight moles of helium. The effective specific heat of the mixture at constant volume is
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
water is heated from to . Ignoring the slight expansion of water, the change in its internal energy is close to (Given specific heat of water ):
EASY
Agniveer Vayu
IMPORTANT
The thermal capacities of two bodies are in the ratio . If the rates of loss of heat are equal for the two bodies under identical conditions of surroundings, then, the ratio of rate of fall of temperature of the two bodies is,
