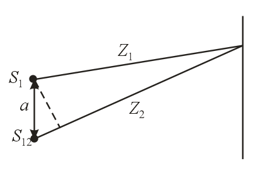
Two identical coherent sources of light, and , separated by a distance produce an interference pattern on a screen. The wavelength of the monochromatic light emitted by the sources is . Determine the maximal number of interference fringes that can be observed assuming that the screen is infinitely large.


Important Questions on Optics
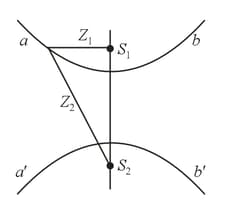
When there is interference of light waves emitted by two coherent sources, the geometric locus of points with the same difference in the phases of the oscillations that arrive at that point from the two sources constitules a surface whose sections with the plane of the drawing are the curves and shown in the figure. What is this surface
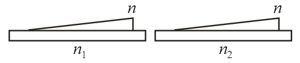
A transparent dielectric is deposited in the form of a thin film on two substrates made of different dielectrics. Both films iorm geometrically identical wedge-like layers. The refractive index of the material of the film is and those of the substrates are and , with . Suppose that two light beams of similar spectral composition fall on the two systems at the same angle. In what respects do the resulting interference patterns differ?
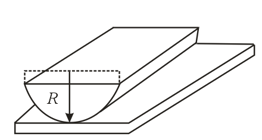
A plano-convex lens with a radius of curvature is lying on a reflecting cylindrical surface whose radius of curvature is . The lens is illuminated from above. What shape do the interference fringes have?
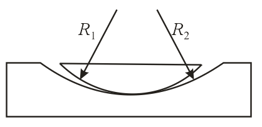
A plano-convex segment of a glass cylinder whose curvature radius is is lying on a flat plate. A parallel beam of light falls on this segment from above. What shape will the interference fringes have and how will the distance between the fringes change as we move away from the straight line along which the segment touches the plate?
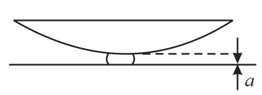
During observation of Newton rings, a small particle of unknown thickness got between the lens and the plate. How can one determine the wavelength of monochromatic light incident from above on the lens using only graphical considerations? What scales along the vertical and horizontal axes are preferable?
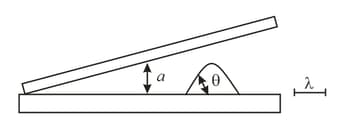
On a reflecting substrate there lies a transparent plane-parallel plate that forms an angle with the substrate. Thus a wedge-like film of air is formed. The substrate has a triangular ledge whose cross section is an isosceles triangle with angles at its base. The plate is illuminated with monochromatic light from above. Assuming that the angles and are small, sketch the positions of the interference Fringes. The size of the wavelength is shown in the Figure.