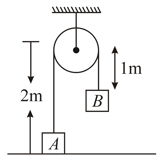
Two masses each of are suspended by a light inextensible string passing over a smooth massless pulley such that mass rest on smooth table & is held at the position shown. Mass is now gently lifted up to the pulley and allowed to fall from rest. Determine up to what height(in ) will rise for the ensuing motion.


Important Questions on Centre of Mass, Momentum and Collisions
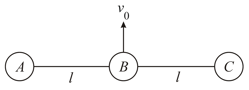
Three identical balls each of mass are connected with each other as shown in figure. and rest over a smooth horizontal table. At moment , ball is imparted a horizontal velocity . Calculate velocity of just before it collides with ball .
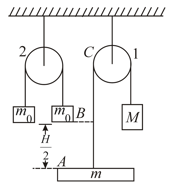
Consider the system shown in figure. We know the masses of bodies: . The distance are covered in equal time intervals by the body of mass and at it undergoes an elastic collision with a stationary body of mass (unknown). Time after this collision when the string in pulley becomes tight again is . is in second. is equal to . Value of is. (Given : ) (Take: )
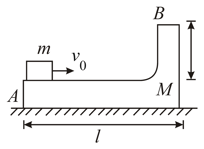
A wedge of mass rests on a smooth horizontal plane. A small block of mass rests over it at left end as shown in figure. A sharp impulse is applied on the block, due to which it starts moving to the right with velocity) . At highest point of its trajectory, the block collides with a particle of same mass moving vertically downwards with velocity and gets stuck with it. If the combined body lands at the end point of body of mass , calculate length in . Neglect friction )
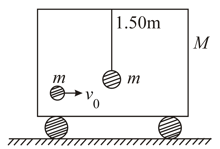
A ball of mass is hung vertically by a thread . Upper end of the thread is attached to the ceiling of a trolley of mass . Initially, trolley is stationary and it free to move along horizontal rails without friction. A shell of mass moving horizontally with velocity collides with the ball and gets stuck with it. As a result, thread starts to deflected towards right. Calculate its maximum deflection in degrees with the vertical.
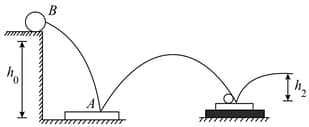
A ball dropped from a height reaches a height after bouncing twice from identical plates. Plate A rests directly on hard ground, while plate rests on a foam -rubber mat. Determine.
(i) the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the plates,
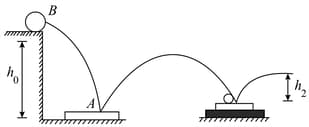
A ball dropped from a height reaches a height after bouncing twice from identical plates. Plate A rests directly on hard ground, while plate rests on a foam -rubber mat. Determine.
(ii) the height of the ball's first bounce.