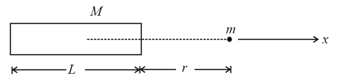
Two objects attract each other by gravitational force . If mass of one object is doubled, the gravitational force between these objects will be
Important Questions on Gravitation
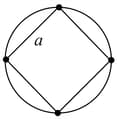
Four identical particles of mass are located at the corners of a square of side . What should be their speed if each of them revolves under the influence of other’s gravitational field in a circular orbit circumscribing the square?
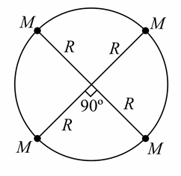
Four particles each of mass move along a circle of radius under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction as shown in figure. The speed of each particle is :
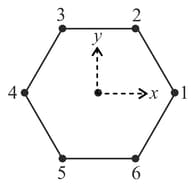
Six objects are placed at the vertices of regular hexagon. The geometric centre of the hexagon is at the origin with objects and on the -axis (see figure). The mass of the th object is where is an integer, is constant with dimension of mass and is the angular position of the th vertex measured from the positive -axis in the counter-clockwise sense. If the net gravitational force on body at the centroid vanishes, the value of is
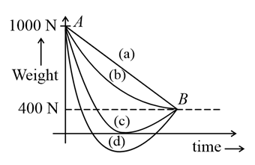
A person whose mass is travels from Earth to Mars in a spaceship. Neglect all other objects in sky and take acceleration due to gravity on the
surface of the Earth and Mars as and , respectively. Identify from the below figures, the curve that fits best for the weight of the passenger as a function of time.