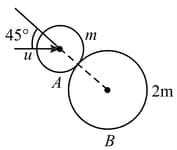
Two smooth spheres made of identical material having masses ' ' and ' ' undergoes an oblique impact as shown in figure. The initial velocities of the masses are also shown. The impact force is along the line joining their centres. The coefficient of restitution is Calculate the velocities of the masses after the impact.


Important Questions on Impulse and Collision
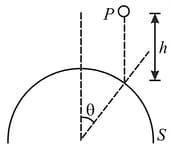
A hemisphere and a particle are of same mass 'm'. is dropped from a height ' '. A hemisphere is kept on a smooth horizontal surface. The particle collides elastically with hemisphere at the point shown in the figure. If and after collision the velocity of the particle becomes horizontal. Find the velocities of hemisphere ' ' and particle ' ' after collision.
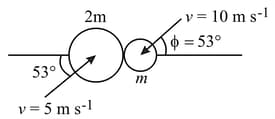
Disc of mass collides with stationary disc of mass as shown in figure. Find the value of coefficient of restitution for which the two discs move in perpendicular direction after collision.
A mass with initial speed in the positive -direction collides with a mass which is initially at rest at the origin, as shown in figure. After the collision moves off with speed in the negative -direction, and moves off with speed at angle
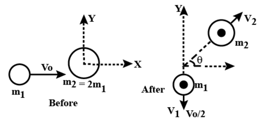
(a) Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the centre of mass before the collision, as well as its velocity after the collision.
(b) Find in terms of
A smooth ball ' 'travels towards another identical ball ' with a velocity Ball is at rest and the impact parameter is equal to where is radius of each ball. Due to impact the direction of motion of ball changes by Find the velocities of the balls ' ' and ' 'after collision. It is given that collision is elastic.
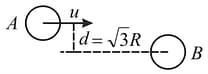
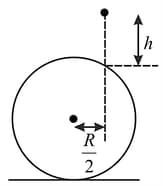
A small particle of mass is released from a height on a large smooth sphere kept on a perfectly smooth surface, as shown in the figure. Collision between particle and sphere is perfectly inelastic. Determine the velocities of particle and sphere after collision.
Sand is falling on a flat car being pulled with constant speed. The rate of mass falling on the cart is constant. Then the horizontal component of force exerted by the falling sand on the cart,
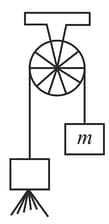
A mass is connected by a weightless cable passing over a frictionless pulley to a container of water, whose mass is at If the container ejects water in downward direction at a constant rate With a velocity relative to the container, determine the acceleration of as a function of time.