EASY
Earn 100
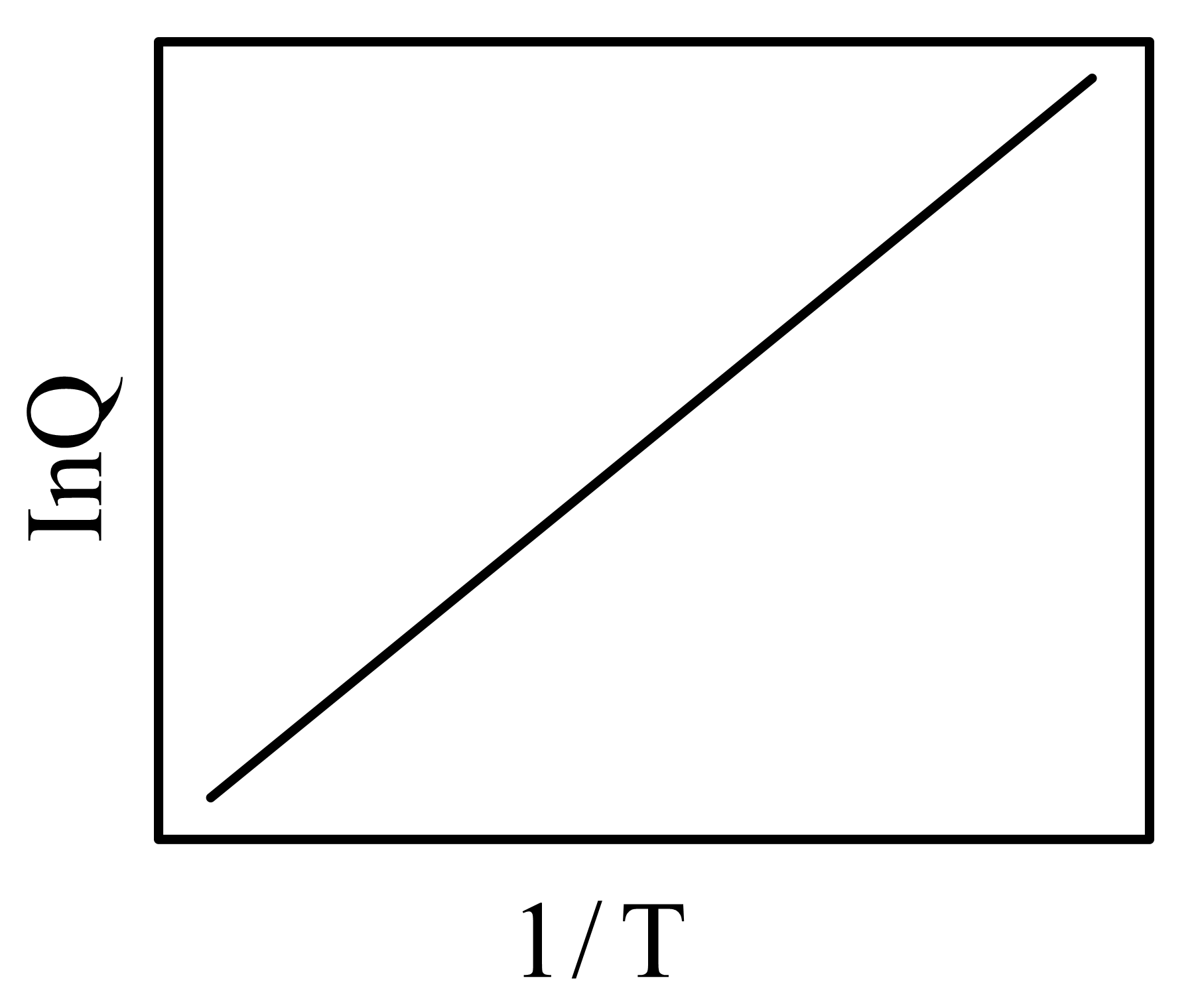
Two vessels and contain aqueous solutions of a weak acid and its salt , respectively. The following two equilibria and , exist in vessels and , respectively. At equilibrium (at a given temperature ), the concentrations of and in vessel are and , respectively, while that of and in vessel , are and , respectively. Let the quantity be denoted by . The correct plot vs is
(a)
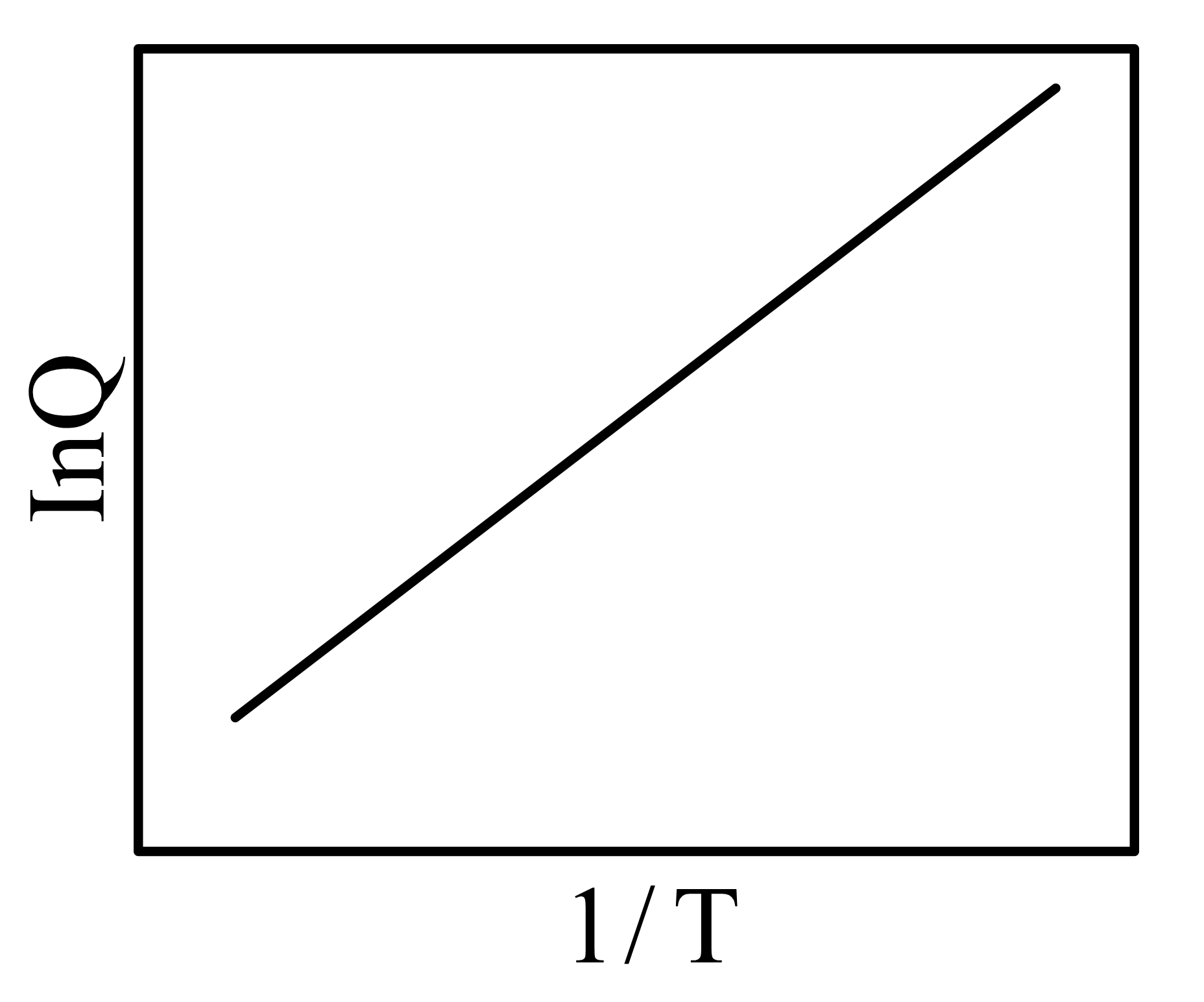
(b)
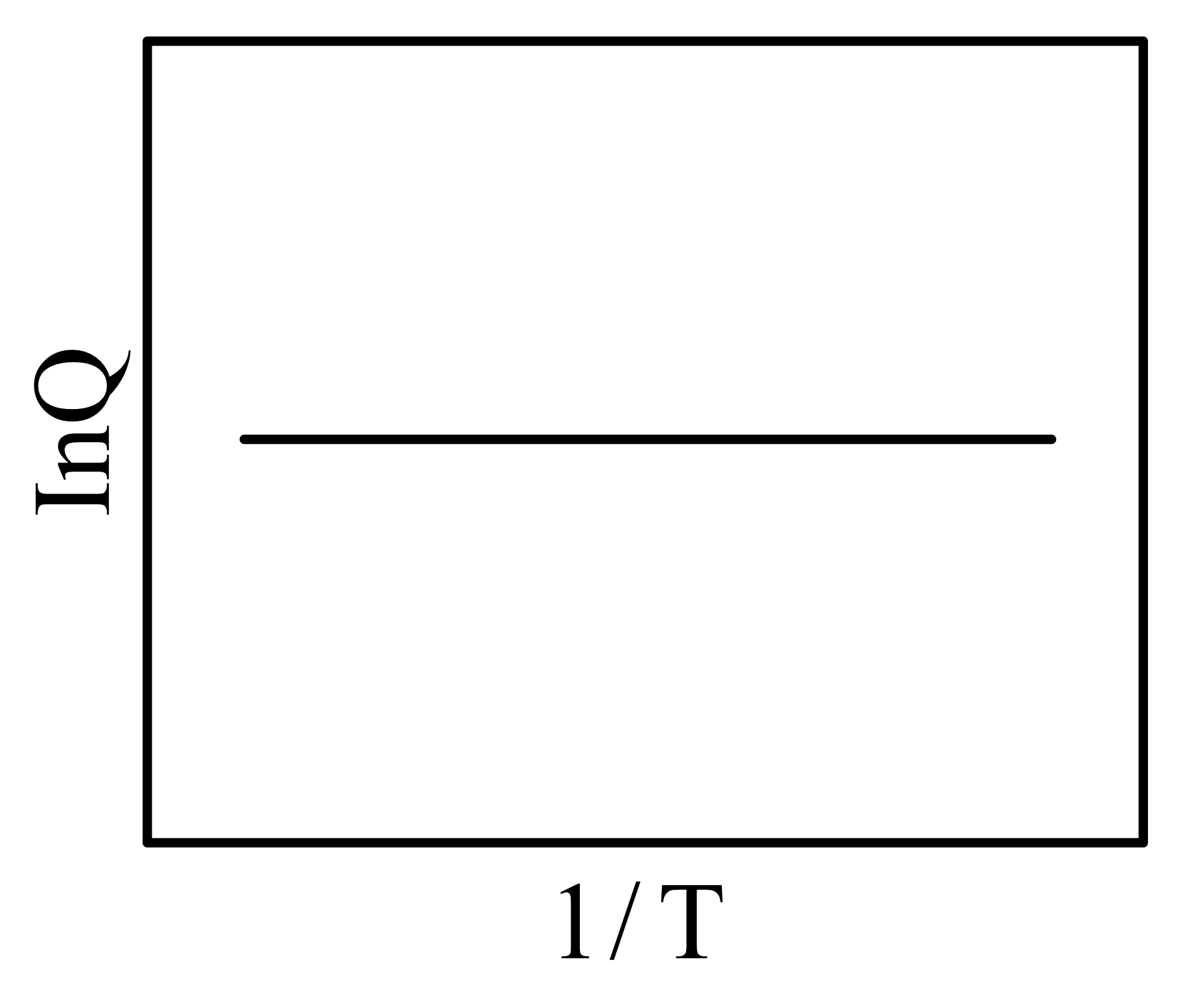
(c)
(d)
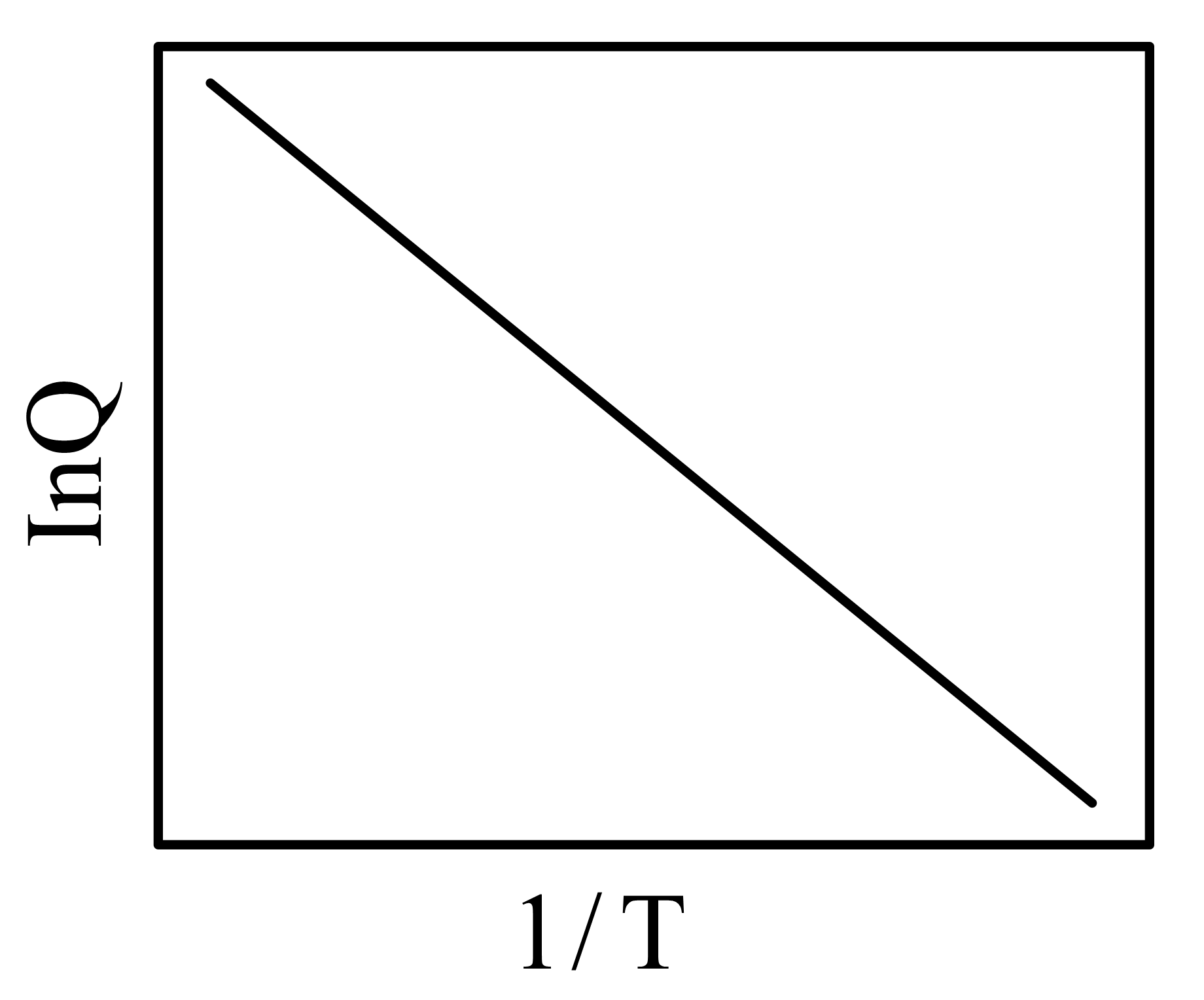
75% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Equilibrium
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion and the other is labelled as Reason .
Assertion :Phenolphthalein is a dependent indicator, remains colourless in acidic solution and gives pink colour in basic medium
Reason : Phenolphthalein is a weak acid. It doesn't dissociate in basic medium.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
HARD
EASY
| List-1 Acid |
List-2 Ka(ionization constant) |
||
| A) | I) | ||
| B) | II) | ||
| C) | III) | ||
| D) | Niacin | IV) | |
| V) | |||
The correct match is
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
moles of a weak acid is dissolved in of solution. The degree of dissociation of is __________ (Round off to the Nearest Integer). [Neglect volume change on adding and assume degree of dissociation ]
MEDIUM
HARD
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
The degree of dissociation of acetic acid in water is
( of acetic acid is )
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
aqueous solution of at is _________ (Nearest integer)
MEDIUM

