Under normal physiological conditions, every 100 ml of oxygenated blood can deliver around 5 ml of O2 to the tissues. The physiological conditions favouring this exchange have?
Important Questions on Breathing and Respiration
Study the following forms of transport of respiratory gases
A) as bicarbonates
B) through plasma
C) as carbamino compounds
D) through
E) in a dissolved state
Arrange the above in sequence in ascending order based on their percentages.
In the given graph curves and represent the relation between partial pressure of oxygen and saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen. If curve represents the condition of blood in a regular artery then please select the correct statement from below.
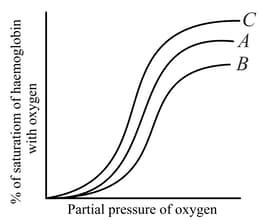
Select the favourable conditions required for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin at the alveoli.
Study the following oxygen-haemoglobin dissociation curve which explains the effect of pH on the saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen. Find out an option that gives the correct descending order of pH for and
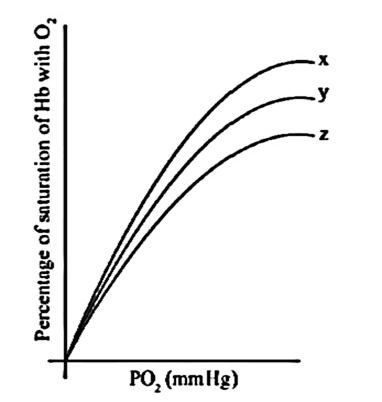
A) Carbonic anhydrase converts 20 molecules of in an hour
B) By attaching the substrate to the enzyme active site, the structure of the substrate get transformed into products
C) Stability of the structural state is related to enzyme status of the molecule
D) The difference between average energy content of the substrate and that of the transition state is called activation energy

