Use of anti–transpirant may check
Important Questions on Transport in Plants
Study the diagram and the list given below.
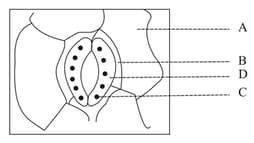
i) Chloroplast
ii) Epidermal cell
iii) Guard cell
iv) Subsidiary cell
v) Stomatal pore
The correct match is
Identify the correct match of the type of water given in column-I and its character in column-II and select the correct option.
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| (i) | Capillary water | (a) | present in the form of hydrated oxides of silicon and aluminium. |
| (ii) | Hygroscopic water | (b) | goes down through large pores between soil particles and reaches the water table. |
| (iii) | Combined water | (c) | held in between small non-colloidal soil particles. |
| (iv) | Gravitational water | (d) | held tightly around soil particles by adhesive forces. |
Given below is a diagram of the stomatal apparatus. Match the labels with the corresponding names of the compounds.
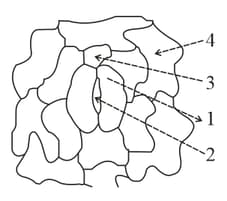
Choose the correct combination.
Choose the correct answer from each of the four options given below:
Which one of the following does not affect the rate of transpiration?
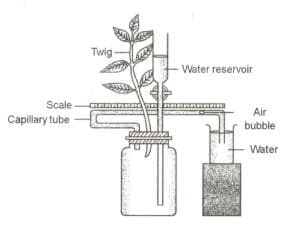
Given below is an apparatus that was set up to investigate a physiological process in plants. The setup was placed in bright sunlight. Answer the questions that follow:

(i) Name the process being studied. Define the process.
(ii) Why was the pot enclosed in a rubber sheet?
(iii) Mention two external factors which can accelerate the above process.
(iv) List two adaptations in plants to reduce the above process.
(v) Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a stomatal apparatus.
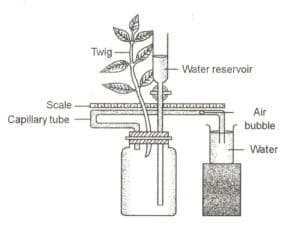
Observe the apparatus carefully and then answer the questions that follow:
State the use of water reservoir.
Give suitable explanation for the following:
Cork and bark of trees help in preventing loss of water.
Observe the apparatus carefully and then answer the questions that follow:
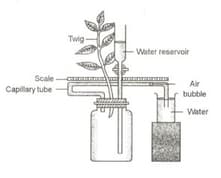
Name the apparatus.
Observe the apparatus carefully and then answer the questions that follow:
State the purpose of this apparatus.