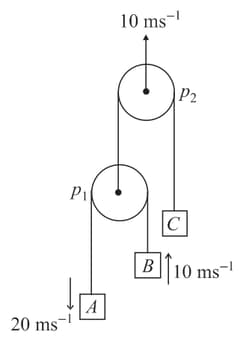
Velocities of blocks and pulley are shown in the figure. Find velocity of pulley and block .


Important Questions on Laws of Motion
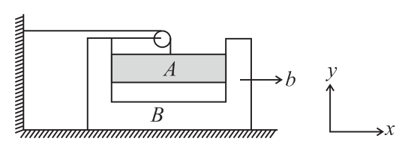
Find the acceleration of block in terms of acceleration of wedge as shown in figure.
In the figure, the tension in the string between the points and is .
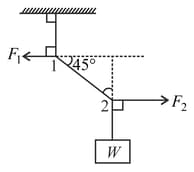
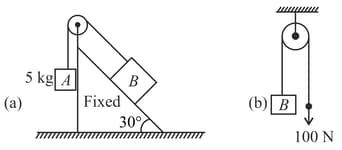
(a) Find the magnitude of the horizontal force and which must be applied to hold the system according to the position shown in figure.
(b) What is the weight of the suspended block?
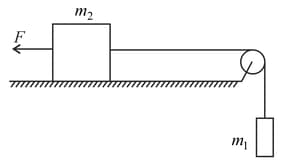
A constant force is applied on the block of mass as shown in the figure. The string and the pulley are light and the surface of the table is smooth. Find the acceleration of .
A chain consisting of five links each with mass is lifted vertically with constant acceleration of as shown. Find
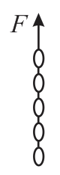
(a) the forces acting between adjacent links.
(b) the force exerted on the top link by the agent lifting the chain.
(c) the net force on each link.
Find out the acceleration of the block in the following systems.
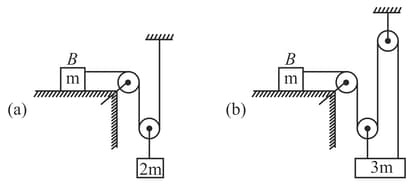
Find out the mass of block to keep the system at rest .
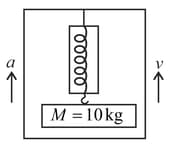
A man of mass is standing on a weighing machine placed in a lift moving with velocity and acceleration as shown in the figure. Calculate the reading of the weighing machine in the following situations:

(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
(vii)
(viii)
What will be the reading of spring balance in the figure shown in following situations .
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
(vii)
(viii)
