EASY
Earn 100
What are conjugate foci for a spherical mirror?
Important Questions on Reflection of Light
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
| Column 1 | Column 2 | ||
| (A) | (a) | Convex mirror | |
| (B) | (b) | Concave mirror | |
| (C) | (c) | Real image | |
| (D) | (d) | Virtual image |
MEDIUM
A point object is moving uniformly towards the pole of a concave mirror of focal length along its axis as shown below. The speed of the object is . At , the distance of the object from the mirror is . The average velocity of the image formed by the mirror between time and is:
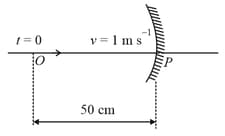
HARD
MEDIUM
| Object pin | Convex Lens | Convex Mirror | Image Pin |
| 22.2 cm | 32.2 cm | 45.8 cm | 71.2 cm |
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
HARD
MEDIUM
Represent the union of two sets by Venn diagram for each of the following.
is a prime number between and
is an odd number between and
HARD
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
HARD

