EASY
Earn 100
What are the factors which affect vapour pressure?
Important Questions on Solutions
HARD
HARD
EASY
MEDIUM
(
)
MEDIUM
Which of the following relations is correct?
MEDIUM
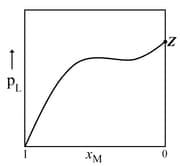
HARD
(Given that the vapour pressure of pure liquid A is at temperature )
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
(molar mass of urea )
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
The vapour pressure vs. temperature curve for a solution solvent system is shown below.
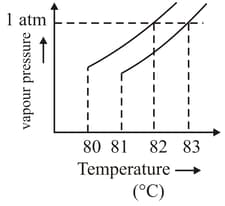
The boiling point of the solvent is _____°C.
EASY
MEDIUM

