EASY
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
What are the two focal length of a lens? Are they equal?

Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces : Lenses
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
The image of a candle is formed by a convex lens on a screen. If the lower half of the lens is painted black to make it completely opaque, will still the full-size image of the candle be obtained?
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
What will be the effect on focal length and nature of a lens when immersed in a liquid whose refractive index is less than that of the material of the lens?
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A concave mirror and a concave lens are held in water. What changes, if any, do you expect in their focal lengths as compared to their values in air?
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
Can a convex (converging) lens behave as a concave (diverging) lens in some situation? Give example.
EASY
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A convex lens forms the image of the sun at a distance of . Where will the image be formed, if a lens of the same power but of double the aperture is used?
EASY
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A convex lens forms the image of the sun at a distance of . Where will the image be formed, if a lens of the same aperture but of double the power is used?
MEDIUM
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
In the figure shown, is a point object placed in the air on the axis of a spherical surface of a glass block. is an incident ray. The direction of the refracted ray in the glass block is parallel to the principal axis . is the radius of the spherical surface. Use the formula to show that the object distance ; where and .
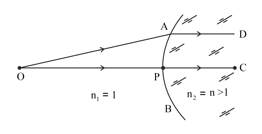
HARD
12th ICSE
IMPORTANT
A monochromatic ray of light is incident on a spherical refracting surface of refractive index . If and be the first and second focal lengths of the surface, show that .
