What causes the bicuspid valve to close during ventricular systole?

Important Questions on Transport in Mammals
Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in different forms. Describe how carbon dioxide molecules reach red blood cells from the respiring cells.
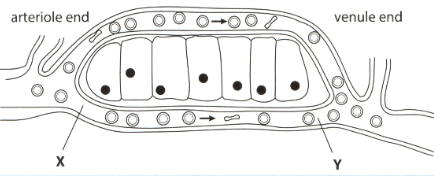
The diagram above shows part of a capillary network and surrounding tissues.
State three ways in which the blood at Y differs from the blood at X other than the concentration of carbon dioxide.
An enzyme in red blood cells catalyses the reaction between carbon dioxide and water as the blood flows through the respiring tissues.

Name the enzyme that catalyses this reaction.
An enzyme in red blood cells catalyses the reaction between carbon dioxide and water as the blood flows through the respiring tissues.
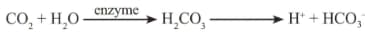
Explain the significance of this reaction in the transport of carbon dioxide.
The graph below shows the effect of increasing the effect of carbon dioxide concentration.
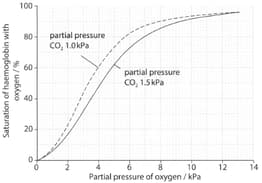
State the percentage saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen at a partial pressure of 5 kPa of oxygen when the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is:
- 1.0kPa
- 1.5 kPa
The graph below shows the effect of increasing the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the oxygen dissociation curve for haemoglobin.
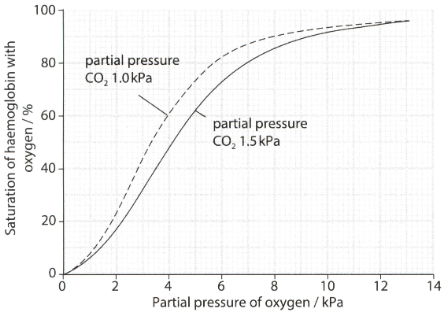
The per cent saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen decreases as the partial pressure of carbon dioxide increases. Explain how this happens?
Name the effect of the increasing carbon dioxide concentration on the oxygen dissociation curve.
The graph below shows the effect of increasing the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the oxygen dissociation curve for haemoglobin.

Explain the importance of the Bohr's effect of carbon dioxide on haemoglobin as shown in the graph.
