MEDIUM
Earn 100
What happens when a dry baking soda is mixed with tartaric acid crystals?
(a)They react slowly.
(b)No reaction takes place.
(c)They react as soon as they are mixed together.
(d)None of these.
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
Consider the given plots for a reaction obeying Arrhenius equation (and are rate constant and activation energy, respectively )
(I)
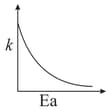
(II)
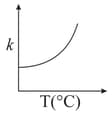
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
(i) time, (ii) concentration of reactants, (iii) temperature, and (iv) catalyst
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
For a reaction, consider the plot of versus given in the figure. If the rate constant of this reaction at is , then the rate constant at is:
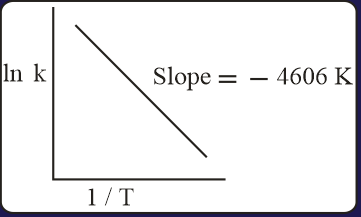
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
For an elementary chemical reaction, , the expression for is:
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
The activation energy of the backward reaction exceeds that of the forward reaction by (in ). If the pre-exponential factor of the forward reaction is times that of the reverse reaction, the absolute value of for the reaction at is ____.
(Given; and is the Gibbs energy)
HARD
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
(Assume that all these gases behave as ideal gases)
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
(a) In which test tube does the reaction proceed faster?
(b) Give reason.
(c) Give an instance in daily life, where such condition is made use.
EASY
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.
MEDIUM
Physical Sciences>Matter and Its Interactions>Apply scientific principles and evidence to provide an explanation about the effects of changing the temperature or concentration of the reacting particles on the rate at which a reaction occurs.>Chemical Reactions - Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy.

