EASY
Earn 100
What is for system that does 500 cal of work on surrounding and 300 cal of heat is absorbed by the system?
(a)-200 cal
(b)-300 cal
(c)+200 cal
(d)+300 cal
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) (ln7.5 = 2.01)
EASY
MEDIUM
HARD
The specific heat of a certain substance is . Assuming ideal solution behavior, the energy required (in ) to heat of molal of its aqueous solution from to is closest to :
[Given: molar mass of the substance ; specific heat of water ]
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
of nitrous oxide gas is cooled at a constant pressure of atm from to causing the compression of the gas from to . The change in internal energy of the process, is . The value of is _____.
[nearest integer]
(Given: atomic mass of and of . Molar heat capacity of is )
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
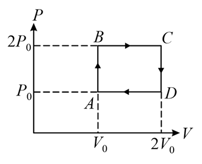
The above diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal mono-atomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle, is:

