What is Avogadro's law?
Important Questions on Kinetic Theory of Gases
Volume-temperature graph at atmospheric pressure for a monoatomic gas ( is
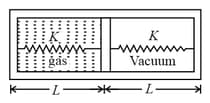
Area of piston is . When heat is supplied to the gas it expands and displaces piston by , where . Natural length of springs is . Spring constant . The pressure of gas in final situation is – (considering equilibrium)
A blend of nitrogen and water vapour is admitted to a flask at , which contains a sufficient solid drying agent. After a long time, the pressure reached a steady value of If the experiment is done at and drying agent in weight increases by , determine the volume of the flask. Also, neglect any possible vapour pressure of drying agent and volume occupied by the drying agent.
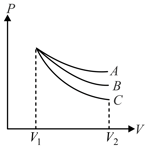
An ideal gas undergoes an expansion from a state with temperature and volume through three different polytropic processes and as shown in the diagram. If and be the magnitude of change in internal energy along the three paths respectively, then
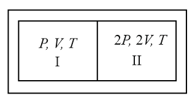
The temperature of a gas contained in a closed vessel of constant volume increases by when the pressure of the gas is increased by . The initial temperature of the gas is
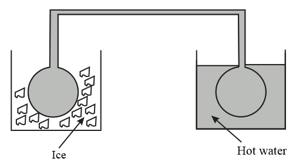
Two identical glass bulbs are interconnected by a thin glass tube at . A gas is filled in these bulbs. If one bulb is placed in ice and another bulb is placed in hot bath, the pressure of the gas become times. The temperature of hot bath will be.
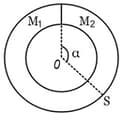
A ring-shaped tube contains two ideal gases with equal masses and molar masses M1 = 32 and M2 = 28. The gases are separated by one fixed partition and another movable stopper S which can move freely without friction inside the ring. The angle is