EASY
Earn 100
What is Down-syndrome?
Important Questions on Principles of Inheritance and Variation
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
A woman heterozygous for colour blindness marries a colour-blind man. What would be the ratios of carrier daughters, colour-blind daughters, normal sons, and colour-blind sons in the F1 generation?
EASY
HARD
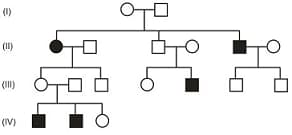
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
HARD
(i) Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease.
(ii) Down's syndrome is due to aneuploidy.
(iii) Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive gene disorder.
(iv) Sickle cell anaemia is an X-linked recessive gene disorder.
EASY
EASY

EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
| Group I | Group II |
| P. Phenylketonuria | i. Melanin synthesis |
| Q. Albinism | ii. Conversion of Phenylalanine to Tyrosine |
| R. Homocystinuria | iii. Tyrosine degradation |
| S. Argininemia | iv. Methionine metabolism |
| v. Urea Synthesis |
HARD
EASY

