What is Earth's critical velocity? Explain.
Important Questions on Matter : Structure and Properties
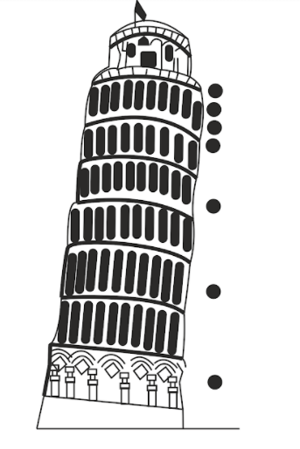
Add dots onto the diagram below to show the pattern you would expect to find for an object with greater mass, but same surface area at same intervals of time.
A ball is dropped from rest. The force of air resistance in the ball is proportional to the ball's speed. Explain why the ball will reach terminal speed.
Consider a primary sedimentation tank (PST) in a water treatment plant with Surface Overflow Rate (SOR) of . What will be the diameter of the spherical particle having percent theoretical removal efficiency in this tank ? Assume that settling velocity of the particles in water is described by Stokes’s Law.
Given: Density of water ; Density of particle ; ; Kinematic viscosity of water

The spacing between the dots in the figure increases gradually. State what tells you about the speed of the falling object.
State what is meant by terminal speed.
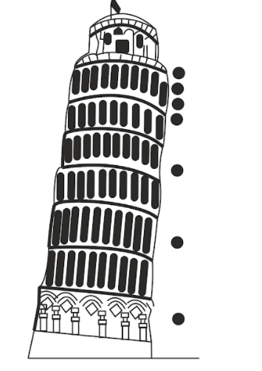
What would be the acceleration you would expect to find for an object with greater mass, but same surface area at same intervals of time.
A skydiver jumps out of an aircraft and falls vertically downwards.
Sort the sentences into the correct order. Write a number against each sentence. The first one has been done for you.
- The skydiver accelerates. The skydiver goes faster
- The skydiver's parachute opens
- The faster the skydiver falls, the higher the air resistance
- The skydiver slows down before reaching the ground
- Eventually the force due to air resistance matches the weight of the skydiver
- The parachute increases air resistance
When this happens, the acceleration is zero and the skydiver falls at a speed called terminal speed (velocity)

