HARD
Earn 100
What is a lever? Explain its principle.
Important Questions on Simple Machine
EASY
The diagram below shows a claw hammer used to remove a nail:
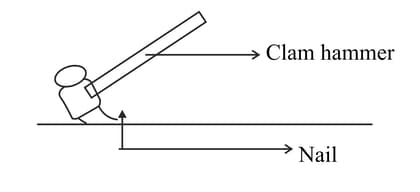
(i) To which class of lever does it belong?
(ii) Give one more example of the same class of lever mentioned by you in (i) for which the mechanical advantage is greater than one.
HARD
The diagram below shows a pulley arrangement:

Copy the diagram and mark the direction of tension on each stand of the string.
What is the velocity ratio of the arrangement?
If the tension acting on the string is, then what is the relationship between and effort ?
If the free end of the string moves through a distance , find the distance by which the load is raised.
MEDIUM
(a) Name the pulleys A, B, and C.
(b) Mark in the diagram the directions of load (), effort () and tension and in the two strings.
(c) How are the magnitudes of and related to the tension ?
(d) Calculate the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio of the arrangement.
(e) What assumptions have you made in parts (c) and (d)?
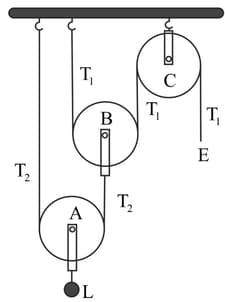
EASY
EASY
EASY
In a single fixed pulley, the velocity ratio is always more than the mechanical advantage.
MEDIUM
A seesaw .
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
(a) In the diagram, mark the direction of tension on each strand of string.
(b) What is the purpose of the pulley ?
(c) If the tension is , deduce the relation between and .
(d) What is the velocity ratio of the arrangement?
(e) Assuming that the efficiency of the system is . What is the mechanical advantage?
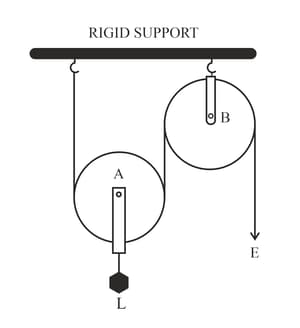
EASY
MEDIUM
Forceps .
MEDIUM
EASY

