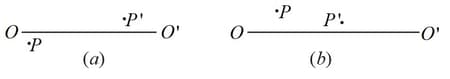What is linear and angular aperture.
Important Questions on Reflection and Spherical Mirror
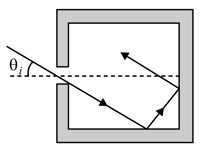
A monochromatic beam of light enters a square enclosure with mirrored interior surfaces at an angle of incidence (see the figure below). For some value(s) of , the beam is reflected by every mirrored wall (other than the one with opening) exactly once and exists the enclosure through the same hole. Which of the following statements about this beam is correct?
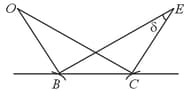
The image of an object due to reflection from the surface of a lake is elongated due to the ripples on the water surface caused by a light breeze. This is because the ripples act as tilted mirrors as shown below. Consider the case, where and the observer are at the same height above the surface of the lake. If the maximum angle that the ripples make with the horizontal is , then the angular extent of the image will be
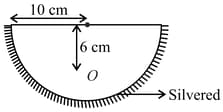
A hemispherical glass body of radius 10 cm and refractive index 1.5 is silvered on its curved surface. A small air bubble is 6 cm below the flat surface inside it along the axis. The position of the image of the air bubble made by the mirror is seen :
A ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a spherical mirror falls at a point as shown in the figure below:
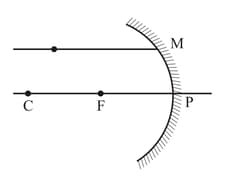
Identify the type of mirror used in the diagram.
The figure below depicts a concave mirror with centre of curvature focus , and a horizontally drawn as the optic axis. The radius of curvature is and . A ray of light , parallel to the optical axis and at a perpendicular distance from it, is incident on the mirror at . It is reflected to the point on the optical axis, such that . Here is a measure of lateral aberration.
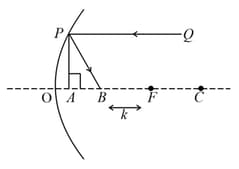
(a) Express in terms of .
(b) Sketch
(c) Consider points on the concave mirror which are increasingly further away from the optic centre and approximately equidistant from each other(see figure below). Rays parallel to the optic axis are incident at and reflected to points on the optic axis. Consider the points where these rays reflected from intersect the rays reflected from respectively. Qualitatively sketch the locus of these points in figure below for a mirror (shown with solid line) with radius of curvature .
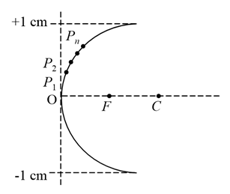
By means of plotting, find:
the path of a light ray after reflection from a concave and convex spherical mirrors (see the figure, where is the focal point and is the optical axis);
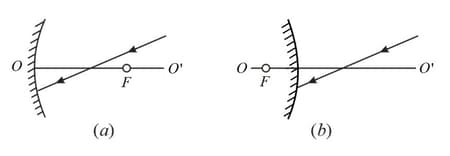
the positions of the mirror and its focal point in the cases illustrated in the figure, where and are the conjugate points.