EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Earn 100
What is meant by the term ideal gas?

Important Questions on States of Matter
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Under what conditions do real gases differ from ideal gases? Give reasons for your answer.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Calculate the volume occupied by 272 g of methane at a pressure of 250 kPa and a temperature of 54 °C.
(R = 8.31 JK–1mol–1; Mr methane = 16.0)
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
The pressure exerted by 0.25 mol of carbon monoxide in a 10 dm3 flask is 120 kPa. Calculate the temperature in the flask in Kelvin.
(R = 8.31 JK–1mol–1)
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
When 0.08g of liquid X was vaporised at 100 °C, 23 cm3 of vapour was formed. The atmospheric pressure was 1.02 × 105 Pa. Calculate the relative molecular mass of liquid X.
(R = 8.31 JK–1mol–1)
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
A flask of volume 2 x 10-3 m3 contains 4.19 g of a gas. The pressure in the flask is 300 kPa and the temperature is 20°C. R = 8.31 J K-1 mol -1.
You can find the relative molecular mass using the expression:
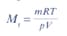
Which one of the following gives the correct value for the relative molecular mass of the gas?

EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Bromine is a reddish-brown liquid. Some liquid bromine is placed in a closed jar. The bromine starts to evaporate. The colour of the vapour above the liquid bromine becomes darker and darker. After a time the bromine vapour does not get any darker. Use ideas about moving particles to explain these observations.
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Explain the following: why are most metals strong, but ionic solids are brittle?
EASY
AS and A Level
IMPORTANT
Explain the following:
why is an alloy of copper and tin stronger than either copper or tin alone?
