EASY
Earn 100
What is sex differentiation?
Important Questions on Principles of Inheritance and Variation
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
Match the following?
| List I | List II | List III | |||
| a) | Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD | i) | Y- linked | p) | Impair blood clotting |
| b) | Hypertrichosis | ii) | Sex limited | q) | Expression is limited to only one sex |
| c) | Haemophilia | iii) | - linked recessive | r) | Progressive weakening of muscles |
| d) | Baldness | iv) | Holandric | s) | Excessive growth of hair on the pinna |
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
In which of the organism, the following type of sex determination is possible
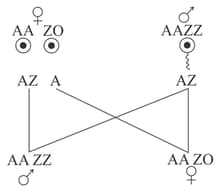
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
Statement I : All the three types of allosomal genes - linked, linked and linked are present only in male human being.
Statement II : Only linked and not linked genes are present in female human being.
The correct option among the following is
EASY
MEDIUM
All given traits are sex limited, except
EASY
HARD
Study the two cases carefully. What would be the correct interpretation of the two cases?
| Case | Mother | Father | Children |
| Case | With disease | Normal | Sons always with diseases |
| Case | With disease | Normal | Sons and daughters could show disease |
MEDIUM
HARD
Match column I and column II and select the correct option:
| Column – I | Column – II | ||
| (A) | Hypertrichosis | (i) | Sex influenced trait |
| (B) | Pattern baldness | (ii) | X – linked recessive trait |
| (C) | Haemophilia | (iii) | Y – Linked trait |
| (D) | Antlers in male deer | (iv) | Sex – limited trait |

