EASY
Earn 100
What is synapse?
Important Questions on Neural Control and Coordination
EASY
Each neuron has a cell body, axon, and dendrites. The dendrites are the protoplasmic extensions of the nerve cell. The axodendritic type of chemical synapse is formed by the association between the axon terminal of the pre-synaptic neuron and the dendrites of a post-synaptic neuron. The action potential causes the fusion of the synaptic vesicle to release the neurotransmitters for neurotransmission. Select the correct option from the following.
EASY
Give an account of synaptic transmission.
EASY
Give an account of synaptic transmission,
MEDIUM
Receptor sites for neurotransmitters are present on
EASY
Action potential in neurons is generated by a rapid influx of
MEDIUM
Select the incorrect statement regarding synapses:
HARD
Explain the plasma membrane of a nerve cell with respect to the maintenance of potential.
EASY
Nissl bodies are mainly composed of
MEDIUM
When 'A' stands for Axon, 'D' for Dendrites, 'S' for Synapse and 'B' for Cell body, a typical sequence of structures between a receptor and an efferent is
MEDIUM
Assertion (A): Impulse transmission across electrical synapse is always faster than that of chemical synapse.
Reason (R): In electrical synapse, pre and post synaptic membranes are in very close proximity and have links called gap functions.
The correct option among the following is
EASY
Stimulation of a muscle fiber by a motor neuron occurs at:
MEDIUM
Which one of the following ion pairs is involved in nerve impulses?
EASY
The transport of which neutrotransmitter is interfered by cocaine?
EASY
The correct pathway of conduction of impulses through a neuron is :
EASY
Assertion (): In myelinated nerve fibres, action potentials are conducted at a faster rate.
Reason (): The myelin present between nodes of Ranvier has concentrated and voltage-gated channels.
EASY
Neurotransmitter released at the neuromuscular junction of a voluntary muscles is:
EASY
Resting membrane potential of a neuron is approximately:
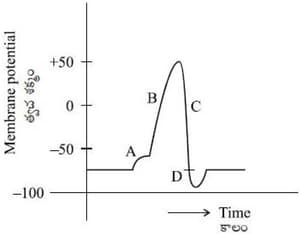
MEDIUM
Identify and in the following graph regarding nerve impulse transmission.
EASY
Concentration of ions outside a nerve cell is times more than inside. The concentration of ions is more inside the cells. The levels of ions and ions are maintained by:
EASY
The potential difference across the membrane of nerve fibre when it does not show any physiological activity is called resting potential. It is about

