What is the center of charge?
Important Questions on Electrostatics
A uniformly charged solid sphere of radius R has potential (measured with respect to ) on its surface. For this sphere the equipotential surfaces with potential and have radius , and respectively. Then
Note : This question had two option correct at the time of examination. Proper corrections are made in the question to avoid it.
Eleven equal point charges, all of them having a charge are placed at all the hour positions of a circular clock of radius except at the position. What is the electric field strength at the centre of the clock?
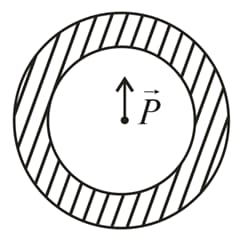
Shown in the figure is a shell made of a conductor. It has inner radius and outer radius , and carries charge . At its centre a dipole is placed as shown then:
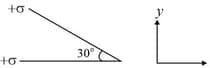
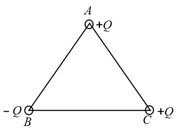
Three charges are placed at the three vertices of an equilateral triangle of side as shown in the figure. The force experienced by the charge placed at the vertex in a direction normal to is
( mass of charged particle)
An infinite number of point charges, each carrying charge, are placed along the y-axis at
The total force on a point charge, placed at the origin, is . The value of , to the nearest integer, is ___ .
[Take ]
What will be the magnitude of the electric field at point as shown in the figure? Each side of the figure is and perpendicular to the other?
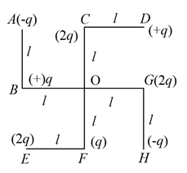
Four point charges are located at the corners of a square of side The force acting on a charge of placed at centre of the square is


