What is the position of secondary maxima and minima?
Important Questions on Wave Optics
replaced by red light, then the diffraction bands _______.
In the Fraunhofer diffraction experiment, the first minima of red light () is formed at the first maxima of another light of wavelength . Find the value of .
A diffraction pattern obtained from a double slit illuminated with monochromatic light is shown in the figure. The dotted line in the figure shows the diffraction envelope while the solid lines give the double slit interference fringes. The experimenter has an arrangement to keep the separation between the slits fixed, but varies the width of the slits. The intensities of the peaks marked by and are and respectively. If the slits are made narrower while keeping the separation fixed, then the ratio
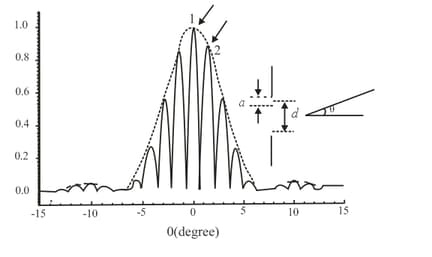
Draw a labelled graph of the intensity of diffracted light versus angle in the Fraunhofer diffraction experiment for a single-slit diffraction.
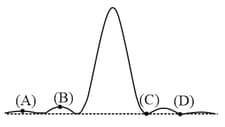
Diffraction pattern from a single slit is shown in the figure. The point at which the path difference between two extreme rays from the slit is twice the wavelength is given by the point
When the frequency of the light used is changed from to , the angular width of the principal (central) maximum in a single slit Fraunhofer diffraction pattern changes by radian. What is the width of the slit (assume that the experiment is performed in vacuum)?

