EASY
Earn 100
What is the primary force driving mass movements?
(a)Gravity
(b)Wind
(c)Water
(d)Ice
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Locomotion and Movement
EASY
EASY
EASY
HARD
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
EASY
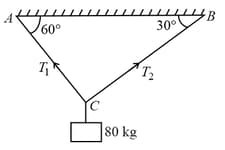
EASY
Was Aristotle correct about his statement aristotle's fallacy? If correct, explain his statement with an illustration.
HARD
MEDIUM
MEDIUM
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
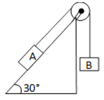
HARD
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY

