What will happen to the following equilibrium reaction if pressure is applied on it?
Important Questions on Equilibrium
The rate of this reaction is increased by
The value of for the reaction
The value of for the following reaction is :
When and are compared at It is found that
The reaction
is in equilibrium in a closed vessel at The partial pressure (in atm) of in the reaction vessel is closest to:
[Given: The change in Gibbs energies of formation at and bar for
Gas constant ]
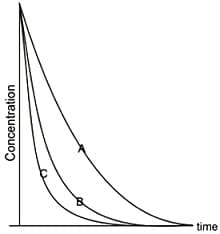
These profiles imply that the decay constants and follow the order
Using the data provided, find the value of equilibrium constant for the following reaction at and atm pressure.
At equilibrium, the mass of each of the reactants and products remains constant.
At equilibrium, the rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction.
Find the total pressure of cases over a mixture of X and Y, when two solid compounds 'X' and 'Y' dissociates at a certain temperature is as follows:
If and are equilibrium constants for the reactions and , respectively, then find out the equilibrium constant for the reaction .
When mole of and mole of are mixed in a closed container at a constant temperature, mole of is obtained at equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium amount of and .
In which direction does the reaction tend to shift to reach equilibrium given at a particular time, the analysis shows that composition of reaction mixture is 3.0 mol L-1 N2, 2.0 mol L-1 H2 and 0.5 mol L-1 NH3.
Equilibrium constant, Kc for the below reaction is

