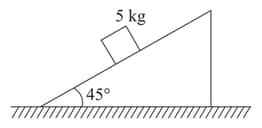
When a block moves down a smooth inclined plane of inclination , its velocity on reaching the bottom is . When it slides down a rough inclined plane of same inclination, its velocity on reaching the bottom is , where is a number greater than . The coefficient of friction between the block and the rough surface is
Important Questions on Friction
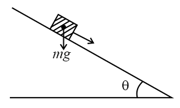
Consider a block kept on an inclined plane (inclined at ) as shown in the figure. If the force required to just push it up the incline is times the force required to just prevent it from sliding down, the coefficient of friction between the block and inclined plane is equal to :
 .
.
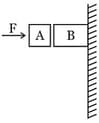
Given in the figure are two blocks and of weight and , respectively. These are being pressed against a wall by a force and kept in equilibrium as shown. If the coefficient of friction between the blocks is and between block and the wall is , the frictional force applied by the wall on block is:
A brick of mass slides down an incline of height and angle If the coefficient of friction of the incline is the velocity of the block at the bottom of the incline is (Assume the acceleration due to gravity is
A block of mass is kept against an accelerating wedge with a wedge angle of to the horizontal. The co-efficient of friction between the block and the wedge is . What is the minimum absolute value of the acceleration of the wedge to keep the block steady. Assume