When a candle burns in the air, carbon dioxide and water are made. The mass of a candle before burning was . The mass of the candle after minutes of burning was .
Calculate the rate at which the candle burnt in .

Important Questions on Chemical Reactions
Explain why the mass decreased?
Look at the graph. It shows how the proportion of carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere has changed over the past years. The unit ‘ppm’ means parts per million.
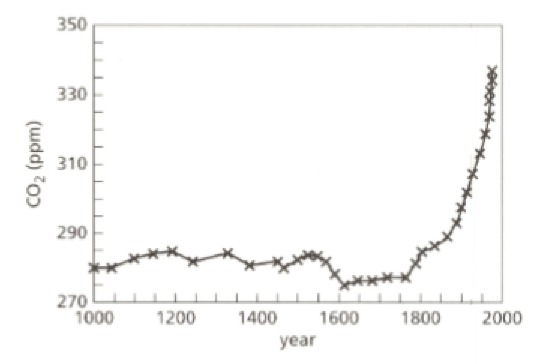
- Describe how the proportion of carbon dioxide changed between and .
Look at the graph. It shows how the proportion of carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere has changed over the past years. The unit ‘ppm’ means parts per million.
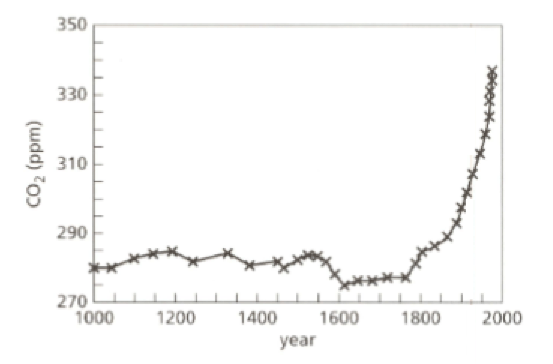
- Give a reason which might explain the changes after the year .
Candle investigation:
Mr Yung’s class are investigating candles. He sets up the following equipment and asks the students to make a prediction.
Mingxia thinks the candles will burn for the same time because the beakers are the same size. Elizaveta thinks the shortest candle will go out first because the carbon dioxide produced will sink to the bottom of the beaker and put the flame out.
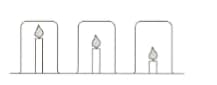
- Explain why Elizaveta thinks that the carbon dioxide will sink?
Candle investigation:
Mr Yung’s class are investigating candles. He sets up the following equipment and asks the students to make a prediction.
Mingxia thinks the candles will burn for the same time because the beakers are the same size. Elizaveta thinks the shortest candle will go out first because the carbon dioxide produced will sink to the bottom of the beaker and put the flame out.
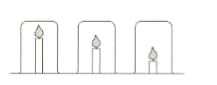
- EpIain why Mr Yung chose beakers that were the same size?
Candle investigation:
Mr Yung’s class are investigating candles. He sets up the following equipment and asks the students to make a prediction.
Mingxia thinks the candles will burn for the same time because the beakers are the same size. Elizaveta thinks the shortest candle will go out first because the carbon dioxide produced will sink to the bottom of the beaker and put the flame out.
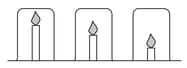
Each group timed how long it took for the lighted candles to go out. Here are the results from Mingxia’s group.
| Candle length in | Time candle burned in seconds | |||
| Experiment | Experiment | Experiment | Mean | |
| _____ | ||||
| _____ | ||||
- Complete the table by working out the mean results. The first one has been done for you.
Candle investigation:
Mr Yung’s class are investigating candles. He sets up the following equipment and asks the students to make a prediction.
Mingxia thinks the candles will burn for the same time because the beakers are the same size. Elizaveta thinks the shortest candle will go out first because the carbon dioxide produced will sink to the bottom of the beaker and put the flame out.
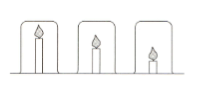
Each group timed how long it took for the lighted candles to go out. Here are the results from Mingxia’s group.
| Candle length in | Time candle burned in seconds | |||
| Experiment | Experiment | Experiment | Mean | |
| _____ | ||||
| _____ | ||||
- Write a conclusion by comparing the means of the results.
Candle investigation:
Mr Yung’s class are investigating candles. He sets up the following equipment and asks the students to make a prediction.
Mingxia thinks the candles will burn for the same time because the beakers are the same size. Elizaveta thinks the shortest candle will go out first because the carbon dioxide produced will sink to the bottom of the beaker and put the flame out.
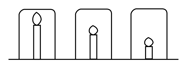
Each group timed how long it took for the lighted candles to go out. Here are the results from Mingxia’s group.
| Candle length in | Time candle burned in seconds | |||
| Experiment | Experiment | Experiment | Mean | |
| _____ | ||||
| _____ | ||||
- Comment on the quality of the data collected in the different experiments.
