EASY
Earn 100
Which one is the correct SI unit of universal gas constant.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Thermal Properties of Matter
MEDIUM
The average distance between molecules of an ideal gas at STP is approximately of the order of
HARD
Two non-reactive monoatomic ideal gases have their atomic masses in the ratio 2 : 3. The ratio of their partial pressures, when enclosed in a vessel kept at a constant temperature, is 4 : 3. The ratio of their densities is
EASY
For the diagram given for an ideal gas
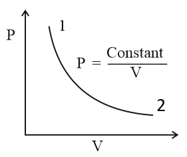
Out of the following which one correctly represents the diagram?
EASY
The state of an ideal gas was changed isobarically. The graph depicts three such isobaric lines. Which of the following is true about the pressures of the gas?
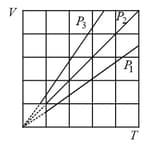
EASY
The temperature of an open room of volume increases from to due to the sunshine. The atmospheric pressure in the room remains . If and are the number of molecules in the room before and after heating, then will be:
MEDIUM
An ideal gas follows a process described by (C is a constant). Then
HARD
A long cylindrical pipe of radius is closed at its upper end and has an airtight piston of negligible mass as shown. When mass is attached to the other end of piston, it moves down by a distance, before coming to equilibrium. Assuming air to be an ideal gas, (see figure) is close to , one atmospheric pressure is ),
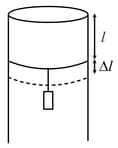
MEDIUM
The equation of state for of oxygen at a pressure and temperature , when occupying a volume will be
MEDIUM
An ideal gas filled in a cylinder occupies volume, . The gas is compressed isothermally to the volume, . Now the cylinder valve is opened and the gas is allowed to leak keeping the temperature the same. What percentage of the number of molecules escape to bring the pressure in the cylinder back to its original value.
HARD
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a linear process as shown in the figure below. Its temperature expressed as a function of volume, is-
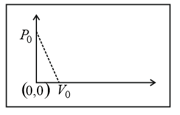
EASY
Modern vacuum pumps can evacuate a vessel down to a pressure of atm. at room temperature (300 K). Taking R = 8.3 JK-1 mole-1, 1 atm = 105 Pa and , the mean distance between molecules of gas in an evacuated vessel will be of the order of :
MEDIUM
A vertical closed cylinder is separated into two parts by a frictionless piston of mass and of negligible thickness. The piston is free to move along the length of the cylinder. The length of the cylinder above piston is and that below the piston is such that Each part of the cylinder contains moles of an ideal gas at equal temperature If the piston is stationary, its mass will be given by:
( is universal gas constant and is the acceleration due to gravity)
HARD
An open glass tube is immersed in mercury in such a way that a length of extends above the mercury level. The open end of the tube is then closed and sealed and the tube is raised vertically up by additional . What will be length of the air column above mercury in the tube now ?
(Atmospheric pressure = of Hg)
MEDIUM
An ideal gas undergoes a circular cycle centred at , as shown in the diagram.
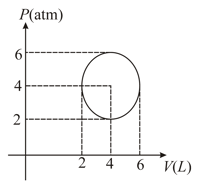
The maximum temperature attained in this process is close to
MEDIUM
One mole of an ideal gas passes through a process where pressure and volume obey the relation . Here and are constants. Calculate the change in the temperature of the gas if its volume changes from to .
MEDIUM
The change in the magnitude of the volume of an ideal gas when a small additional pressure is applied at a constant temperature, is the same as the change when the temperature is reduced by a small quantity at constant pressure. The initial temperature and pressure of the gas were and respectively. If then value of in is __________
MEDIUM
Three moles of an ideal gas are in a rigid cubical box with sides of length . The ratio of the forces that the gas exerts on each of the six sides of the box when the gas temperature are and is.
EASY
A cylinder closed at both ends is separated into two equal parts ( each) by a piston impermeable to heat. Both the parts contain the same masses of gas at a temperature of and a pressure of . If now the gas in one of the parts is heated such that the piston shifts by , then the temperature and the pressure of the gas in this part after heating is
EASY
A given sample of an ideal gas occupies a volume, at a pressure, and absolute temperature, . The mass of each molecule of the gas is . Which of the following gives the density of the gas?
EASY
Universal gas constant is

