Which one of the following sets of phenomena would increase on raising the temperature?
Important Questions on Matter in our Surroundings
Match the column A with column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Liquid state to solid-state. | a. Sublimation |
| 2. Solid-state to a liquid state. | b. Freezing |
| 3. Liquid state to gaseous state. | c. Melting |
| 4. Solid-state to a gaseous state. | d. Condensation |
| 5. Gaseous state to liquid state. | e. Vaporisation |
The substance X normally exists in a physical state which can flow easily but does not fill its vessel completely. It also turns anhydrous copper sulphate blue. When substance X is cooled excessively, it changes into a substance Y which has a fixed shape as well as a fixed volume. If however, the substance X is heated strongly, it changes into a substance Z which has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume.
(a) Name the substances (i) X (ii) Y and (iii) Z.
(b) What is the process of conversion of X into Y known as?
(c) At which temperature X gets converted into Y?
(d) What is the process of conversion of X into Z known as?
(e) At which temperature X gets converted into Z?
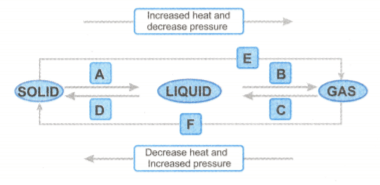
Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
The scientists now say that there are actually five states of matter A, B, C, D, and E. State A has a fixed volume but no fixed shape. State B can be compressed very easily by applying pressure and state C has a fixed shape as well as a fixed volume. State D is a mixture of free electrons and ions whereas state E is named after an Indian scientist and a famous physicist.
(a) Name the physical states (i) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D, and (v) E.
(b) Name one substance belonging to state C which can directly change into vapours on heating. What is this process known as?
(c) Name one substance that normally belongs to state B but whose solid form changes directly into a gaseous state.
(d) Name the most common substance belonging to state A.
(e) Which state of matter makes the sun and other stars to glow.
(a) What is the value of temperature x in Kelvin?
(b) What is the process P known as?
(c) What is the name of energy released during process P?
(d) What is the process Q known as?
(e) What is the name of energy absorbed during process Q?
(a)
(b)
(c)
In the given figure, the inter conversions of matter have been given. The processes involved in the
inter conversions have been marked as A, B, C, D, E and F.
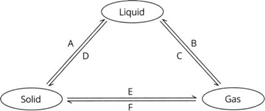
a. Name the processes marked as A, B, C, D, E and F.
b. On cooling a liquid, it changes to a new state. Name the state.
c. When a liquid is heated, it changes to a new state. Name the state.
d. When temperature is lowered and the pressure of a gas is increased, what change is expected?
What are the two ways in which the physical states of matter can be changed?

