White light is incident normally on a diffraction grating with a slit-separation of . The visible spectrum has wavelengths between and .
(a) Calculate the angle between the red and violet ends of the first-order spectrum.

Important Questions on Superposition of Waves
White light is incident normally on a diffraction grating with a slit-separation of . The visible spectrum has wavelengths between and .
(b) Explain why the second-and third-order spectra overlap.
Rays of light from two coherent sources produces constructive interference. Which of the following cannot be the phase difference between these two rays?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(a) Copy the waves shown in the diagram onto a sheet of graph paper and use the principle of superposition to sketch the resultant wave.
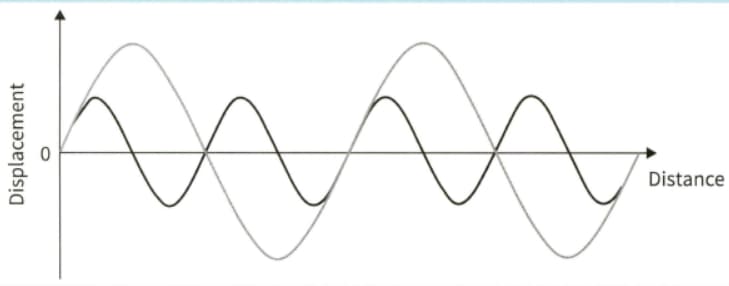
(b) Compare the wavelength of the resultant wave with that of the component waves.
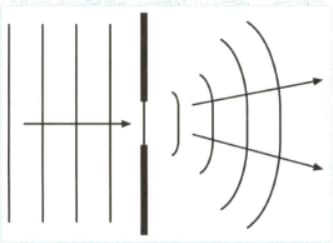
State how the diffracted pattern will change when:
(a) The wavelength of the incident wave is increased
State how the diffracted pattern will change when:
(b) The wavelength of the incident wave is decreased.
